0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views26 pagesExpt3 LabLecture
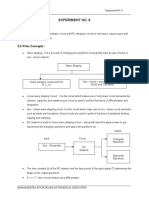
The document outlines Experiment 3, which focuses on the sampling and reconstruction of analog signals using the IC211 Kit. It details the hardware features, including an 8-bit DAC and ADC, and describes the procedures for monitoring DAC output, using ADC with internal DC input, and signal digitization and reconstruction. Additionally, it includes instructions for observing ADC input and DAC output waveforms at various frequencies.
Uploaded by
amit.gangurde003Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views26 pagesExpt3 LabLecture
The document outlines Experiment 3, which focuses on the sampling and reconstruction of analog signals using the IC211 Kit. It details the hardware features, including an 8-bit DAC and ADC, and describes the procedures for monitoring DAC output, using ADC with internal DC input, and signal digitization and reconstruction. Additionally, it includes instructions for observing ADC input and DAC output waveforms at various frequencies.
Uploaded by
amit.gangurde003Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26