0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views9 pagesMADT
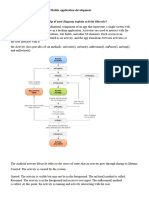
The document provides an overview of various Android development concepts, including UI thread management, adapters, event handling, mobile operating systems, storage options, application components, and services. It also covers Android's architecture, fragments, notifications, and the use of PhoneGap for cross-platform development. Additionally, it explains the lifecycle of activities and fragments, as well as the importance of the AndroidManifest.xml file.
Uploaded by
katetanmay5115Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views9 pagesMADT
The document provides an overview of various Android development concepts, including UI thread management, adapters, event handling, mobile operating systems, storage options, application components, and services. It also covers Android's architecture, fragments, notifications, and the use of PhoneGap for cross-platform development. Additionally, it explains the lifecycle of activities and fragments, as well as the importance of the AndroidManifest.xml file.
Uploaded by
katetanmay5115Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9