Darius Sayar
20 April 2025
Project 7
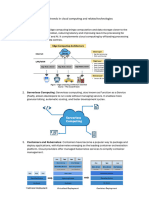
Definitions
- Cloud backup: A strategy for sending copies of files or databases to remote servers for
preservation in case of failure or disaster
- Public cloud: Cloud services delivered over the public Internet and shared among
multiple customers
- Private cloud: Cloud infrastructure operated solely for a single organization, managed
internally or by a third party
- Cloud bursting: A configuration that directs overflow traffic from a private cloud to a
public cloud when demand peaks
- SaaS: Software applications delivered over the Internet, hosted and managed by the
provider
- PaaS: A development environment in the cloud that provides tools and services to build,
test, and deploy applications
- IaaS: Virtualized computing resources (compute, storage, networking) provided on a
pay-as-you-go basis
- Utility computing: A service model where computing resources are metered and billed
based on usage rather than a flat rate
Company 1: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the leading cloud provider, offering a broad set
of global services that help organizations move faster, lower costs, and scale their applications.
● Compute: Virtual servers and serverless compute, including Amazon EC2, AWS
Lambda, Amazon ECS/EKS, and AWS Fargate
● Storage: Scalable storage services such as Amazon S3, EBS, and Glacier for object,
block, and archival storage
● Database: Managed database services like Amazon RDS (relational), DynamoDB
(NoSQL), and Aurora
● Networking & Content Delivery: Virtual networks, load balancing, and Amazon
CloudFront CDN
● Analytics: Data warehousing and analytics services, including Amazon Redshift and
AWS Glue
● Machine Learning: Prebuilt AI services (SageMaker, Rekognition) for building,
training, and deploying ML models
● Security, Identity, & Compliance: Services such as AWS IAM, AWS Shield, and
Amazon GuardDuty
Company 2: Microsoft Azure Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud platform offering over
600 services across global data centers.
� ● Compute: Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Functions (serverless), and Azure Kubernetes
Service
● Storage: Azure Blob Storage, Disk Storage, and Azure Files for object, block, and file
shares
● Database: Azure SQL Database, Cosmos DB (multi-model), and Azure Database for
PostgreSQL/MySQL
● Networking: Virtual Network, Azure Load Balancer, ExpressRoute, and Content
Delivery Network
● AI & Machine Learning: Azure Cognitive Services and Azure Machine Learning
● Analytics: Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Data Factory
● Security & Identity: Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD), Azure Defender, and
Azure Key Vault
Comparison
Category AWS Azure
Compute EC2, Lambda, ECS/EKS, Fargate Virtual Machines, Functions, AKS
Storage S3, EBS, Glacier Blob Storage, Disk Storage, Files
Database RDS, DynamoDB, Aurora SQL Database, Cosmos DB
Networking & VPC, ELB, CloudFront Virtual Network, Load Balancer, CDN
CDN
Analytics & Redshift, SageMaker Synapse, ML Studio
ML
Security & IAM, Shield, GuardDuty Entra ID, Defender, Key Vault
Identity
References
1. "Cloud Services – AWS Cloud Services," Amazon Web Services. (aws.amazon.com)
2. "Compute on AWS," Amazon Web Services. (aws.amazon.com)
3. "Directory of Azure Cloud Services," Microsoft. (azure.microsoft.com)
4. "Types of Cloud Computing – Definition – Microsoft Azure," Microsoft.
(azure.microsoft.com)
� 5. "What is Cloud Computing?" AWS. (en.wikipedia.org)
6. For definitions:
○ Cloud backup: (techtarget.com)
○ Cloud bursting: (azure.microsoft.com)
○ Utility computing: (en.wikipedia.org)
Research Tools
● Google Search
● Bing Search
● AWS Documentation (aws.amazon.com)
● Microsoft Azure Documentation (azure.microsoft.com)