ACROPOLIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND
RESEARCH
Department of Information Technology
Synopsis
On
Web Scraping
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview:
Project: Web Scraping Automation
Background: Extracting valuable insights from abundant web data is challenging,
requiring automation to streamline data collection.
Objectives: Automate data collection, improve data accuracy, enhance decision-
making.
Technical Stack: HTML, Python, CSS, JavaScript.
Project Scope: Identify data sources, inspect website structures, develop Python
scripts
(BeautifulSoup, Scrapy), implement data storage, handle anti-scraping measures,
ensure data quality, visualize insights (optional).
Deliverables: Web scraping scripts, data storage solutions, documentation,
visualizations.
1.2 Purpose:
Data Collection: For research, market analysis, and academic purposes.
Price Monitoring: Track competitors' pricing to adjust strategies.
Lead Generation: Gather contact info for sales and marketing.
News Aggregation: Compile articles from multiple sources.
�2. LITERATURE SURVEY
2.1 Existing Problem :
Manual Data Collection: Collecting data manually is time-consuming, inefficient,
and prone to errors, especially when dealing with large datasets or frequently updated
information.
Limited Access to Data: Manual methods restrict users to gathering small amounts of
data from individual pages, resulting in incomplete datasets.
Inefficient Data Aggregation: Gathering data from multiple sources manually is slow
and leads to delays in decision-making processes.
2.2 Existing Approaches:
Manual Copying: Manually copying data from websites, which is slow and
unreliable.
APIs: Some websites provide APIs, but they often have data access limitations or
may not be available for all sites.
Outsourcing Data Collection: Hiring third-party services for data collection, which
can be costly and lacks flexibility.
2.2 Proposed Solution:
Web Scraping
Efficiency: It allows for fast and large-scale data collection without manual
intervention.
Comprehensive Data: It can gather complete datasets from multiple sources,
providing more thorough insights.
Real-time Data Access: Scraping tools can continuously update data, ensuring timely
and accurate information.
�3. THEORETICAL ANALYSIS
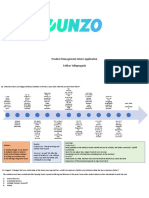
3.1 Block Diagram :
�3.2 Hardware and Software Designing:
Hardware Requirements:
1. Processor: Intel Core i3 or equivalent (for handling multiple requests)
2. RAM: 8 GB or more (for handling large datasets)
3. Storage: 256 GB SSD or more (for storing scraped data)
4. Network: Reliable internet connection (for sending HTTP requests)
Software Requirements:
Operating System:
1. Windows 10 or later
2. macOS High Sierra or later
3. Linux (Ubuntu, CentOS, etc.)
Programming Languages:
1. Python (most popular choice)
2. JavaScript (for browser-based scraping)
3. Ruby (for Ruby-based frameworks)
Web Scraping Frameworks/Libraries:
1. Scrapy (Python)
2. BeautifulSoup (Python)
3. Selenium (Python, JavaScript)
4. Puppeteer (JavaScript)
5. Octoparse (visual scraping tool)
�4. APPLICATIONS
Applications of Web Scraping Automation:
Market Research: Competitor analysis, market trends, customer behavior, pricing.
E-commerce: Price comparison, product cataloging, inventory management, review
analysis.
Finance: Stock data, financial news, company profiles, risk assessment.
Real Estate: Property listings, pricing trends, rental yields, neighborhood analysis.
Travel: Hotel pricing, flight schedules, travel reviews, destination tips.
Web scraping empowers organizations to gather insights, automate tasks, and enhance
decision-making across various sectors, driving growth and innovation
REFERENCES: Udemy
�Guided By: Group Members:
Prof. Monika Chaudhary Jatin Wadhwani (0827IT221070)
Jiya Patel (0827IT221072)
Divya Gupta (0827IT221046)
Divyanshu Pandey(0827IT221047)