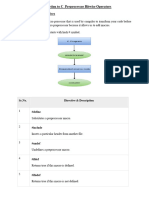
reprocessor directives:- Preprocessor directives are instructions given to the compiler to
P
process the code before actual compilation. These directives start with a #symbol and are
essential for controlling compilation, defining constants, conditional compilation, and more.
No semicolon ; is expected at the end of the Preprocessor directive.
1. #define:-Used to define macros or symbolic constants.
Syntax: #define identifier value
Example:
#define PI 3.14159
#define SQUARE(x) ((x) * (x))
Purpose:-Replaces occurrences of identifierwith valuethroughout the code before
compilation.
Macros can also include arguments, enabling simple inline functions.
Notes:
● No semicolon (;
) is used at the end.
● It does not consume memory, as it's a text substitution.
2. #error:-Generates a compilation error with a specified message.
Syntax:- #error "Error message"
Example:
#if __STDC_VERSION__ < 201112L
#error "C11 support required"
#endif
Purpose:-Stops compilation and displays an error message if certain conditions are met.
3. #include:-Inserts the contents of another file into the source code.
Syntax:- #include <file>
#include "file"
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "myheader.h"
● Angle Brackets (<> ):Used for standard library headers.
● Double Quotes (
"" ):Used for user-defined headers.
Purpose:-Includes code from external files, such as libraries or custom headers.
4.#if:- Tests a condition and includes/excludes code accordingly.
Syntax: #if condition
// code
#endif
Example:
#if defined(DEBUG)
printf("Debugging mode is ON\n");
#endif
� urpose:-Executes code only if the condition evaluates to
P true(non-zero).
5. #else:- Specifies an alternative block of code when the#ifcondition is
false
.
Syntax: #if condition
// code
#else
// alternate code
#endif
Example:
#if DEBUG
printf("Debugging\n");
#else
printf("Production\n");
#endif
6. #elif:-Acts as "else if" for
#if
.
Syntax:
#if condition1
// code
#elif condition2
// code
#else
// alternate code
#endif
Example:
#if OS == 1
printf("Windows\n");
#elif OS == 2
printf("Linux\n");
#else
printf("Unknown OS\n");
#endif
7. #endif:- Ends a preprocessor conditional directive.
Syntax:
#if condition
// code
#endif
#if
Purpose:-Marks the end of a conditional directive like
#ifdef:- Checks if a macro is defined.
8.
Syntax:
#ifdef identifier
� / code
/
#endif
Example:
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("Debug mode enabled\n");
#endif
Purpose:-Includes code only if the macro is defined.
9. #ifndef:-Checks if a macro isnotdefined.
Syntax:-
#ifndef identifier
// code
#endif
Example:
#ifndef MAX
#define MAX 100
#endif
Purpose:-Ensures code is included only if the macro is undefined.
10. #undef:- Undefines a previously defined macro.
Syntax: #undef identifier
Example:
#define DEBUG
#undef DEBUG
Purpose:-Removes a macro definition, making it undefined for subsequent code.