0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views4 pagesData Center
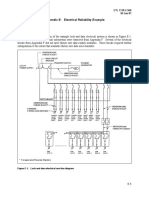
The document outlines various components and systems within a data center, including power distribution methods like Busway, Whip, and Power Distribution Units (PDUs), as well as backup systems like Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS). It also describes cooling solutions such as Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAH) and thermal storage tanks, alongside certifications and design considerations for efficient data center operations. Additionally, it mentions the use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for modeling airflow and the concept of datacenter pods for modular infrastructure management.
Uploaded by
Omar DaoudCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views4 pagesData Center
The document outlines various components and systems within a data center, including power distribution methods like Busway, Whip, and Power Distribution Units (PDUs), as well as backup systems like Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS). It also describes cooling solutions such as Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAH) and thermal storage tanks, alongside certifications and design considerations for efficient data center operations. Additionally, it mentions the use of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for modeling airflow and the concept of datacenter pods for modular infrastructure management.
Uploaded by
Omar DaoudCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4