0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views15 pagesPhysics Project
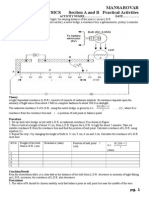
The document outlines a physics investigatory project aimed at determining the refractive index of different liquids using a hollow prism. It includes sections on the aim, apparatus, theory, procedure, observations, conclusions, precautions, and bibliography. The project is guided by Mrs. Jayalaxmi and is intended for the AISSCE 2024-25 practical examination.
Uploaded by
Megha KardakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views15 pagesPhysics Project
The document outlines a physics investigatory project aimed at determining the refractive index of different liquids using a hollow prism. It includes sections on the aim, apparatus, theory, procedure, observations, conclusions, precautions, and bibliography. The project is guided by Mrs. Jayalaxmi and is intended for the AISSCE 2024-25 practical examination.
Uploaded by
Megha KardakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 15