0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views9 pagesNetworking and DBMS
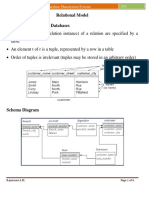
The document provides a comprehensive overview of networking and database management concepts, including types of networks, protocols, IP addressing, OSI and TCP/IP models, and various database management systems. It covers essential topics such as data integrity, SQL commands, normalization, and security measures in both networking and databases. Additionally, it addresses advanced concepts like load balancing, VLANs, and the differences between relational and non-relational databases.
Uploaded by
kartik160614Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views9 pagesNetworking and DBMS
The document provides a comprehensive overview of networking and database management concepts, including types of networks, protocols, IP addressing, OSI and TCP/IP models, and various database management systems. It covers essential topics such as data integrity, SQL commands, normalization, and security measures in both networking and databases. Additionally, it addresses advanced concepts like load balancing, VLANs, and the differences between relational and non-relational databases.
Uploaded by
kartik160614Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9