Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
Summarizing data
Please do not copy without permission. © ALX 2024.
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
Data overview
| You are an analyst hired by an NPO to work on initiatives that focus on closing the gender
achievement gap in education.
You need… The dataset
Summary statistics to help you The PhD graduates in public chartered
understand the gender differences universities in Kenya, 2015 dataset from
among PhD graduates. openAFRICA.
2
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
Data overview
| The PhD graduates dataset contains 22
rows and the following columns:
The dataset
A. Qualification
The title of the qualification being considered.
B. Male
The number of male graduates for each
qualification in the year 2015.
C. Female
The number of female graduates for each
qualification in the year 2015.
3
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
Consider the questions we want to investigate
PhD graduates
PhD graduates
in public chartered
in public universities
chartered in
universities in
KenyaKenya
Which qualifications have
How many males and
How many qualifications the least or most male and
females received PhD
are taken into account? female graduates,
qualifications, respectively?
respectively?
4
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
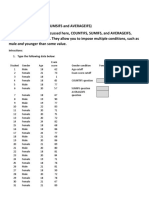
The SUM function
| How many males and females received PhD qualifications, respectively?
The answer to this question will give more information on the
gender disparities among PhD holders at Kenya’s public
chartered universities in 2015.
01. Add all the values in the Male column;
02. Add all the values in the Female column;
5
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The SUM function
The SUM function is used to add the cells that
=SUM(value1, [value2, …]) are specified in the function argument.
The SUM of a range. The SUM of specific cells.
6
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The SUM function
01. Ignores empty cells, cells with text, and 01.
TRUE/FALSE values.
02. Returns an error if any of the cells contain
errors.
02. 02.
7
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The COUNT function
| How many qualifications are taken into account?
This question will provide insight into the number of
qualifications that are taken into account in this study and
give us a better understanding of the scope of the values we
are working with.
Count the number of entries in the
01.
Qualification column;
8
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The COUNT function
The COUNT function counts the number of cells
=COUNT(value1, [value2, …]) that have numerical values within the specified
range.
The COUNT of a range.
9
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The COUNT function
01. Ignores empty cells, cells with text, and 01.
TRUE/FALSE values.
02. Use COUNTA to include text and True/False
values.
03. Ignores cells that contain errors.
02. 03.
10
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The MIN and MAX functions
| Which qualifications have the least or most male and female graduates, respectively?
This inquiry will shed light on the degrees that have
graduated the most or least number of males and females.
This can also help us determine the qualifications that men
and women are more likely to pursue.
Find the minimum and maximum values in the Male
01.
column.
Find the minimum and maximum values in the
02.
Female column.
11
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The MIN and MAX functions
The MIN and MAX functions
=MIN(value1, [value2, …]) find the minimum and =MAX(value1, [value2, …])
maximum number within the
specified range.
The MIN of a range. The MAX of a range.
12
�Data aggregations and descriptive statistics
The MIN and MAX functions
01. Ignores empty cells, cells with text, and
01.
TRUE/FALSE values.
02. Returns an error if any of the cells contain
errors.
02. 02.
13