0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views9 pagesSatellite Communication
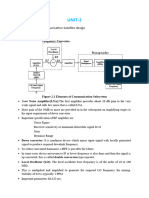
The document outlines the components and processes involved in radio frequency communications, including the roles of transmitters, receivers, modulators, and demodulators. It discusses various frequency bands used for satellite communications and the impact of atmospheric conditions on signal quality, as well as design considerations for communication systems. Additionally, it highlights the importance of noise and interference in communication circuits and the need for careful planning in satellite communication design.
Uploaded by
NaDa AlaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views9 pagesSatellite Communication
The document outlines the components and processes involved in radio frequency communications, including the roles of transmitters, receivers, modulators, and demodulators. It discusses various frequency bands used for satellite communications and the impact of atmospheric conditions on signal quality, as well as design considerations for communication systems. Additionally, it highlights the importance of noise and interference in communication circuits and the need for careful planning in satellite communication design.
Uploaded by
NaDa AlaaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9