0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views25 pagesGetting Started With Windows Server Networking
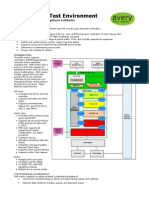
The document outlines a hands-on lab for configuring a Windows Server core network, including tasks such as verifying IPv4 connectivity, establishing DHCP failover, and configuring DNS and Web Application Proxy. It details the setup of a network environment with three servers and a workstation, focusing on essential networking services and configurations. The lab aims to equip participants with the necessary skills to complete the Windows Server Networking challenge series.
Uploaded by
m1d1mansonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views25 pagesGetting Started With Windows Server Networking
The document outlines a hands-on lab for configuring a Windows Server core network, including tasks such as verifying IPv4 connectivity, establishing DHCP failover, and configuring DNS and Web Application Proxy. It details the setup of a network environment with three servers and a workstation, focusing on essential networking services and configurations. The lab aims to equip participants with the necessary skills to complete the Windows Server Networking challenge series.
Uploaded by
m1d1mansonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 25