0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageScript B.ing
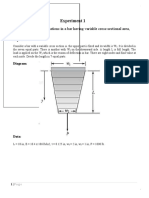
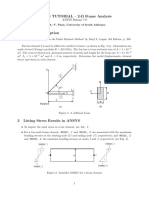
The document outlines a finite element-based simulation process using ANSYS software, which is utilized for modeling and simulating physical behaviors of products. It details the preparation of a steel geometry, meshing, application of boundary conditions, and the forces applied to determine deformation values. The results indicate deformation values ranging from 6.024 millimeters to 24.11 millimeters based on varying applied forces.
Uploaded by
Yogi SaputraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageScript B.ing
The document outlines a finite element-based simulation process using ANSYS software, which is utilized for modeling and simulating physical behaviors of products. It details the preparation of a steel geometry, meshing, application of boundary conditions, and the forces applied to determine deformation values. The results indicate deformation values ranging from 6.024 millimeters to 24.11 millimeters based on varying applied forces.
Uploaded by
Yogi SaputraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1