STRATEGIC FINANCIAL STRUCTURE & PERFORMANCE EVALUATION Long-term Sources of Funds
o Equity Financing - Issuance of stock (common or preferred).
o Debt Financing - Long-term loans and bonds.
FINANCIAL STRUCTURE, CAPITAL STRUCTURES o Leasing - Long-term leasing of assets.
o Retained Earnings - Reinvested profits from the business.
Financial Structure o Venture Capital - External equity for high-growth potential companies.
refers to how a company's assets are financed through various sources, including debt,
equity, and other financial instruments. It includes all types of financial liabilities (long- RECENT APPROACHES TO PROJECT AND CORPORATE FUNDING
term and short-term debt), and equity (common and preferred stock). Crowdfunding: Allows companies to raise capital from a large number of small
investors via online platforms.
Capital Structure
is a subset of financial structure and refers specifically to the composition of long-term Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending: Individuals can lend money to businesses, bypassing
sources of funds used by a firm, such as equity, debt, and hybrid instruments. The traditional financial institutions.
capital structure's primary concern is how these sources are mixed to optimize
Sustainable Finance/Green Bonds: Focuses on funding environmentally and socially
financing costs and minimize risks.
responsible projects.
Composition:
1. Debt
2. Equity THE USE OF FINANCIAL TECHNOLOGY IN CORPORATE FUNDING
3. Hybrid Instruments (Convertible bonds, preference shares) Fintech (Financial Technology) is transforming corporate funding by making access
to finance faster, more transparent, and more decentralized.
Blockchain Technology Provides secure, decentralized platforms for transactions
METRICS FOR ANALYZING FINANCIAL STRUCTURE
and financing, including smart contracts for automating financing terms.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Measures the proportion of debt used relative to equity. A higher Digital Lending Platforms: These platforms streamline loan applications and
ratio indicates greater reliance on debt.
approvals through Al-based assessments.
Leverage Ratio: Shows the degree to which the company is using borrowed money.
Cryptocurrency and Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs): Some companies are using
Cost of Capital (WACC): Weighted average cost of capital reflects the overall cost of cryptocurrencies to raise funds or conduct ICOs to bypass traditional fundraising
capital from all sources, guiding investment and funding decisions. methods.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Credit Scoring: Enhances the evaluation of credit risk,
improving loan approval speed and accuracy.
SHORT-TERM & LONG-TERM SOURCES OF FUNDS
Short-term Sources of Funds
o Trade Credit - Credit extended by suppliers.
o Short-term Loans - Bank loans due within a year.
o Commercial Paper - Unsecured promissory notes issued by companies.
o Bank Overdrafts - Allow companies to withdraw more than what is available in
their accounts.
o Factoring - Selling accounts receivables to improve liquidity.
Page 1 of 5
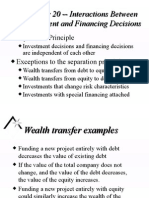
�Capital Projects Evaluation THE IMPACT OF FINANCIAL STRUCTURES ON PLANNING PERFORMANCE
EVALUATION
1. Net Present Value (NPV):
✓ Measures the value added by a project, considering the time value of 1. Leverage and Risk
money. A high-debt structure may increase financial risk, affecting future borrowing capacity
✓ Compares the value of all future cash earnings (adjusted for time) to the and profitability.
upfront cost of an investment to determine if it’s profitable." This means… High Debt = High Risk
Low Debt = Low Risk
NPV Formula: PV of Future Cash Flows - Initial Investment
Illustration: Project: Buy a machine for $1,000 today. It generates: 2. Cost of Capital
Year 1: $500 The mix of debt and equity impacts the company's overall cost of capital, influencing
Year 2: $600 investment decisions and performance outcomes.
Year 3: $700 Debt Financing = Interest Rates
Discount Rate (r): 5% (0.05) Equity Financing = Shareholder’s Returns
= 476.19 + 544.22 + 604.71 – 1,000 Take Note: Equity financing is way more expensive than Debt Financing.
= 625.12 (NPV of total profits in today’s dollars)
3. Flexibility
Evaluation of the project: Good A more equity-heavy structure may provide greater flexibility, allowing companies to
pivot and adjust strategies more easily without the burden of fixed debt payments.
2. Internal Rate of Return (IRR):
✓ The discount rate that makes the NPV of the project equal to zero. 4. Financial Ratios
✓ IRR is the "interest rate" the project effectively pays you on the invested Ratios such as return on equity (ROE) or return on assets (ROA) are directly influenced
capital. by how a company is financed, impacting performance evaluation.
✓ IRR should surpass the hurdle rate (the lowest profit (%) a project must
Debt-heavy companies may look more profitable (high ROE) but are riskier (low
earn to be worth doing.) ROA, high debt ratios).
3. Payback Period: The time required for the investment to generate enough
cash flow to recoup the initial investment. Equity-heavy companies look less profitable (low ROE) but are stable
(no debt pressure).
Note: Equity Structure – does not have the burden of paying the debt
To pivot means..
Changing Product
Changing Audience
Page 2 of 5
�SRATEGIC VALUE ANALYSIS FREE CASH FLOW
refers to the cash generated by a company after accounting for the necessary capital
expenditures required to maintain or expand its asset base.
Short-cut Financial Statement Approach
It represents the amount of cash available for distribution to investors, including both
Many financial analysts consider financial statements as a good reference for valuing equity and debt holders, without jeopardizing the company’s operational sustainability.
business. They argue that using current and previous company accounts as the base
would be fair as actual financial performance is the proof of evidence for a firm’s To turn the financial results into cash flow documents, there are a few steps to
capability to generate revenue and the net assets (at market value) represent the follow:
saleable value of the firm assets. a) Convert the corporate operating plan into operating cash profits plan;
b) Prepare incremental working capital;
Simple short-cut method has shortfalls.
c) Prepare incremental fixed capital investment;
Oversimplifying valuation ignores past data, skips analyzing key business factors, and d) Summarize in a cash flow statement.
fails to identify real performance drivers, leading to uncertainty and potential
Operating Cash Profit
miscalculations.
This is the first step to convert the operating profit into cash profit by adjusting all
Short-cut method is bound to increase valuation errors. Strategic value analysis noncash items so that the statement reflects the actual cash profit position of the
approach can be an alternative for this naïve valuation approach. company.
Incremental Fixed Capital Investment
Firms need additional fixed capital investment to underpin normal operation and
SRATEGIC VALUE ANALYSIS growth.
is an evaluation about firm’s value proposition, value chain, business logics, operating
capabilities, and value drivers that contribute to value creation. Incremental Working Capital
Firms need additional fixed capital investment to underpin normal operation and
STAGES IN CONDUCTING STRATEGIC VALUE ANALYSIS growth.
1. Identification
2. Formulation Incremental Working Capital
3. Valuation Stages Working capital includes inventory, accounting receivable, account payable and
accrued expenses, etc. Companies need working capital to support sales.
*Insert Illustrations
Discount Rate
is the rate used to discount future free cash flows (FCF) to their present value. It
CORPORATE BLUE PRINT (FINANCIAL) represents the required return investors expect based on the risk of the investment.
Strategic value analysis enables the company to identify competitive strengths, decide The discount rate is a crucial component in valuing a company because it accounts for
strategic position, and develop implementation strategies to meet its strategic intent the time value of money and the risk associated with future cash flows.
and goals. These are the work plans of the firm to follow accordingly. Also, these are
the strategic assumptions of the corporate plan.
*Insert figure
Page 3 of 5
�The following are common methods for financial valuation. ✓ The first term refers to risk-free and the second term relates to risk
premium.
1. Heuristics Method
✓ Risk-Free Rate - the risk-free rate portion relates to the most secured
✓ This is an intuitive approach for investors or corporate management
return that can be achieved. CAPM defines risk-free as there is no
based on market or industrial comparable, return on capital employed
variance in expected return or the risk level is approaching zero.
(ROCE), or investors’ view on the risk of the project.
✓ Risk Premium - has beta and market risk premium.
✓ Common method for investment evaluation (especially for corporate
✓ Beta is a tool to measure market risk. CAPM regards this part of market
management).
risk as non-diversifiable because of the market violability by
✓ Simplest way to set discount rate.
macroeconomic factors that cannot be diversifiable.
✓ If the firm has the similar level of violability as the general market, the
2. Dividend Valuation Method
beta value is 1. The firm has the risk same as the general market. The
✓ This approach considers shareholders’ required rate of return by
higher the beta is, the higher the risk the firm bears, the higher will be the
reference to the future dividends stream they anticipate. It is the dividend
expected rate of return from the firm.
yield (%) required by investors for the market value of the investment
✓ If the company beta is 2, it means the firm’s risk is double the general
(e.g., stock).
market risk. In fact, beta data can be acquired from financial information
✓ Used for computation of cost of equity Ke% (shareholders’ portion).
service agents.
✓ Takes into an assumption that dividends grow at a constant rate
✓ Market Risk Premium. This risk premium presents the excess return
perpetually.
above the risk-free rate, the extra risk that the market needs to
compensate investors for risks above risk-free investments. In fact,
market risk premium is the general market risk.
✓ Beta is the multiplier of the market risk premium. When beta is 1, the firm
just bears normal market risks. Investors bear higher than the general
market risk when beta is above 1. The contrary result applies when beta
is lower than 1.
What is the cost of equity of a company if its beta is 2, market risk
premium is 4.5%, and treasury bill is 1%. The cost of equity would be?
Cost of equity = 1% + (2 × 4.5%)
= 10%
If a company has a current dividend per share at $0.8, a market price of $20,
and an expected growth rate of 10%, its cost of equity would be?
4. Weighted Cost of Capital (WACC)
✓ The source of company’s funds is not necessarily provided entirely from
shareholders. Quite contrarily, company would borrow money from banks
or external parties. Both sources of funds have different costs of capital.
3. Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
✓ Therefore, there is a need to calculate the weighted average cost of
✓ This is another model to approximate cost of equity. The model has
capital (WACC) for the company since both debts and equity bear
explicitly split the formula into two terms.
different costs of capital.
✓ Cost of equity = Risk-free rate + (Beta × market risk premium)
Page 4 of 5
� A firm has a total source of funds of $100 million, divided by 20% in debt
portion and 80% in equity portion. The cost of equity is 13% and after tax cost
of debt is 8%. What is the WACC of the company?
Cost of capital (WACC) = 20% × 8 + 80% × 13
= 12%
Business Valuation (Using DCF)
Business valuation using the Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method is a
fundamental approach in finance to estimate the value of a business or
investment based on the present value of its expected future cash flows.
DCF is a valuation method that estimates the value of an investment based
on its expected future cash flows, which are discounted back to their present
value using a discount rate (usually the Weighted Average Cost of Capital, or
WACC).
TAKEAWAY TIPS
• Corporate key strategies are imbedded in the financial blue print.
• Corporate cash flows are the basic inputs for strategic valuation using DCF
method.
• Discount rate (cost of capital) has great impact on calculation of business
value.
• In business valuation, value of the firm beyond the forecast period may be
much greater than the value generated from the forecast period. However,
this terminal value is often ignored.
• Business valuation can be used as a means for strategic value analysis and
monitoring.
Page 5 of 5