0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views18 pagesOOPClass Note
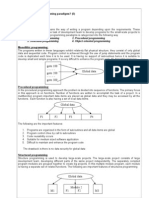
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm centered around objects and their interactions, emphasizing data over functions, and providing features like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It offers advantages such as improved security, easier code modification, and better code reusability compared to procedural programming, which focuses on functions and has limitations in data security and modularity. OOP is applicable in various domains including real-time systems, client-server architectures, and AI expert systems, making it a versatile choice for software development.
Uploaded by
raisheetal683Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views18 pagesOOPClass Note
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm centered around objects and their interactions, emphasizing data over functions, and providing features like encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. It offers advantages such as improved security, easier code modification, and better code reusability compared to procedural programming, which focuses on functions and has limitations in data security and modularity. OOP is applicable in various domains including real-time systems, client-server architectures, and AI expert systems, making it a versatile choice for software development.
Uploaded by
raisheetal683Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18