0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesJDBC Java
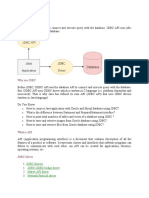
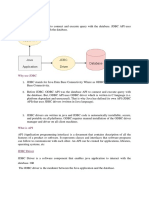
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is a Java API that allows Java applications to connect to and interact with databases using JDBC drivers. There are four types of JDBC drivers: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, Native-API Driver, Network Protocol Driver, and Thin Driver, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The process of connecting to a database using JDBC involves five steps: registering the driver class, creating a connection, creating a statement, executing queries, and closing the connection.
Uploaded by
rohitgaikwad6157Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views9 pagesJDBC Java
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is a Java API that allows Java applications to connect to and interact with databases using JDBC drivers. There are four types of JDBC drivers: JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver, Native-API Driver, Network Protocol Driver, and Thin Driver, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The process of connecting to a database using JDBC involves five steps: registering the driver class, creating a connection, creating a statement, executing queries, and closing the connection.
Uploaded by
rohitgaikwad6157Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9