0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pagesModule 4.1
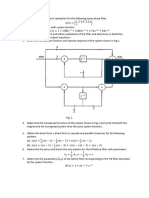
The document discusses the realization of FIR filters in digital signal processing, focusing on two main structures: Direct Form and Cascade Form. It provides mathematical representations and examples for both structures, including linear phase realization and the use of minimum multipliers. Additionally, it references key texts for further reading on digital signal processing.
Uploaded by
soujath048Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pagesModule 4.1
The document discusses the realization of FIR filters in digital signal processing, focusing on two main structures: Direct Form and Cascade Form. It provides mathematical representations and examples for both structures, including linear phase realization and the use of minimum multipliers. Additionally, it references key texts for further reading on digital signal processing.
Uploaded by
soujath048Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18