0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views13 pagesScript 3.0
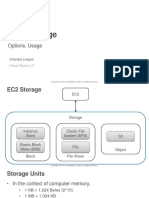
The document introduces Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) as a cloud-based storage solution for AWS EC2 instances, likening it to a virtual hard drive that provides reliable, scalable storage. It explains the functionality of EBS, including its ability to persist independently from EC2 instances and the use of snapshots for data backup. Additionally, it outlines different EBS volume types and their specific use cases, emphasizing the importance of understanding EBS for cloud-based projects.
Uploaded by
shaikirshad4771Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views13 pagesScript 3.0
The document introduces Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) as a cloud-based storage solution for AWS EC2 instances, likening it to a virtual hard drive that provides reliable, scalable storage. It explains the functionality of EBS, including its ability to persist independently from EC2 instances and the use of snapshots for data backup. Additionally, it outlines different EBS volume types and their specific use cases, emphasizing the importance of understanding EBS for cloud-based projects.
Uploaded by
shaikirshad4771Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 13