0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views16 pagesLecture 9 Summary of The Force Method
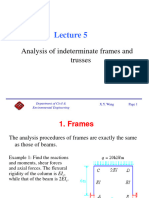
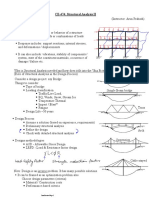
The lecture discusses the force method in structural analysis, focusing on equilibrium equations, compatibility conditions, and constitutive relations. It outlines the procedures for the flexibility method, including determining indeterminacy, calculating displacements, and solving for redundant forces. The advantages and disadvantages of statically indeterminate structures are also highlighted, noting their benefits in stress and deformation management, as well as potential issues from external factors.
Uploaded by
wiltonliu.lpcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views16 pagesLecture 9 Summary of The Force Method
The lecture discusses the force method in structural analysis, focusing on equilibrium equations, compatibility conditions, and constitutive relations. It outlines the procedures for the flexibility method, including determining indeterminacy, calculating displacements, and solving for redundant forces. The advantages and disadvantages of statically indeterminate structures are also highlighted, noting their benefits in stress and deformation management, as well as potential issues from external factors.
Uploaded by
wiltonliu.lpcCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16