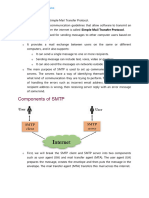
SMTP Architecture
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a protocol used for sending emails from one server to
another.
It operates at the Application Layer of the OSI model and is responsible for email transmission over
the Internet.
Components of SMTP Architecture:
1. User Agent (UA):
- This is the software or email client that the user interacts with to compose, send, and receive
emails.
- Example: Gmail, Outlook, Thunderbird.
- The user creates the email in the User Agent, which forwards the message to the Mail Transfer
Agent (MTA) for sending.
2. Mail Transfer Agent (MTA):
- This is the core part of the SMTP architecture responsible for transferring the email from the
sender's system to the recipient's mail server.
- The MTA sends and receives emails, acting as a relay between email servers.
- Example: Postfix, Sendmail.
- Functions:
- Accepts the message from the User Agent.
- Relays the message to another MTA or delivers it to the final Mail Delivery Agent (MDA).
3. Mail Delivery Agent (MDA):
- This agent receives the message from the MTA and delivers it to the recipient's mailbox.
� - The MDA stores the email until the recipient accesses it through their User Agent.
- Example: Dovecot, Courier.
4. Mail Access Protocol:
- To retrieve the mail from the server, email clients use protocols such as IMAP (Internet Message
Access Protocol) or POP3 (Post Office Protocol).
- While SMTP is used for sending, IMAP and POP3 are used for retrieving emails from the MDA.
SMTP Message Flow:
1. Mail Composition:
- The sender uses a User Agent (e.g., Gmail) to write the email.
- The email is submitted to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA).
2. Mail Transmission:
- The sender's MTA connects to the recipient's MTA using SMTP.
- The email is transferred between MTAs over the internet.
3. Mail Reception:
- Once the email reaches the recipient's MTA, it is passed to the Mail Delivery Agent (MDA).
- The MDA stores the message in the recipient's mailbox.
4. Mail Access:
- The recipient uses their User Agent to access their mailbox via IMAP or POP3.
- The recipient can then read, reply, or forward the email.
Protocols Used:
- SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): Used for sending emails between servers.
�- IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): Used for retrieving emails from the server, allowing
users to access mail from different devices.
- POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3): Also used for retrieving emails, but typically downloads and
removes the email from the server, making it unavailable from other devices.