0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesICT Lecture System and Application Software
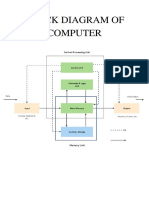
Software is categorized into System Software, which manages hardware and enables applications, and Application Software, which performs specific user tasks. Key components of System Software include Operating Systems, Utility Programs, Device Drivers, and Firmware, while Application Software encompasses Productivity, Media, Web Browsers, Communication, Gaming, and Custom Software. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for effective computer usage.
Uploaded by
cededav956Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesICT Lecture System and Application Software
Software is categorized into System Software, which manages hardware and enables applications, and Application Software, which performs specific user tasks. Key components of System Software include Operating Systems, Utility Programs, Device Drivers, and Firmware, while Application Software encompasses Productivity, Media, Web Browsers, Communication, Gaming, and Custom Software. Understanding the differences between these types is essential for effective computer usage.
Uploaded by
cededav956Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2