0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views17 pagesReadingMaterial SystemCall KernelRecompilation-3
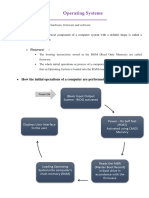
This document provides a comprehensive guide for implementing a new system call in the Linux operating system, including steps for kernel recompilation and user space program integration. It outlines the necessary preparations, modifications, and commands required to successfully add a system call that adds two positive integers. Additionally, it includes practice problems and assignment phases for further learning and implementation.
Uploaded by
statisfy168Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views17 pagesReadingMaterial SystemCall KernelRecompilation-3
This document provides a comprehensive guide for implementing a new system call in the Linux operating system, including steps for kernel recompilation and user space program integration. It outlines the necessary preparations, modifications, and commands required to successfully add a system call that adds two positive integers. Additionally, it includes practice problems and assignment phases for further learning and implementation.
Uploaded by
statisfy168Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17