0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views59 pagesP Block
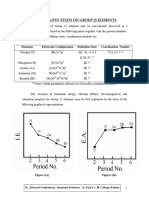
The document discusses the P-block elements, specifically the nitrogen family (Group 15), detailing their electronic configurations, physical properties, catenation tendencies, and chemical reactivity. It highlights the unique characteristics of nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, including their bonding behaviors and the stability of their hydrides. Additionally, it includes information on Unacademy subscriptions for educational resources related to these topics.
Uploaded by
chandrakalabhatt9066Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views59 pagesP Block
The document discusses the P-block elements, specifically the nitrogen family (Group 15), detailing their electronic configurations, physical properties, catenation tendencies, and chemical reactivity. It highlights the unique characteristics of nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth, including their bonding behaviors and the stability of their hydrides. Additionally, it includes information on Unacademy subscriptions for educational resources related to these topics.
Uploaded by
chandrakalabhatt9066Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 59