0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views14 pagesMastering C Pointers - From Basics To Real Applications
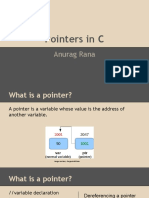
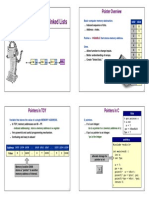
This document is a comprehensive guide to pointers in C programming, covering topics such as pointer declaration, arithmetic, function pointers, and dynamic memory allocation. It includes practical examples, common pitfalls, debugging techniques, and real-world applications, along with interview questions and exercises. The guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of pointers and their usage in various programming scenarios.
Uploaded by
venuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views14 pagesMastering C Pointers - From Basics To Real Applications
This document is a comprehensive guide to pointers in C programming, covering topics such as pointer declaration, arithmetic, function pointers, and dynamic memory allocation. It includes practical examples, common pitfalls, debugging techniques, and real-world applications, along with interview questions and exercises. The guide aims to provide a thorough understanding of pointers and their usage in various programming scenarios.
Uploaded by
venuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14