0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesFactoring
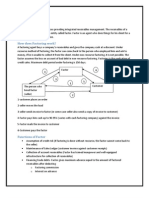
Factoring is a financial service where a business sells its receivables to a third party, known as a factor, at a discount to raise funds. The factor provides various services including credit cover, cash advances, sales ledger maintenance, collection of receivables, and advisory functions, allowing the business to focus on core operations. This service helps businesses manage cash flow and mitigate risks associated with credit and collections.
Uploaded by
ayswaryaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesFactoring
Factoring is a financial service where a business sells its receivables to a third party, known as a factor, at a discount to raise funds. The factor provides various services including credit cover, cash advances, sales ledger maintenance, collection of receivables, and advisory functions, allowing the business to focus on core operations. This service helps businesses manage cash flow and mitigate risks associated with credit and collections.
Uploaded by
ayswaryaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3