0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views8 pagesCost Accounting 2 Marks
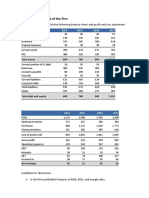
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cost accounting concepts, including output costing, retention money, work certified, normal loss, by-products, and various costing methods such as activity-based costing and job costing. It also includes calculations for ton kilometers, passenger kilometers, and profit reconciliation, along with definitions of key terms like abnormal gain, operating costing, and marginal costing. Additionally, the document outlines the treatment of abnormal loss and gain, along with the significance of break-even points and the valuation of stock in cost and financial accounts.
Uploaded by
xyz065993Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
102 views8 pagesCost Accounting 2 Marks
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cost accounting concepts, including output costing, retention money, work certified, normal loss, by-products, and various costing methods such as activity-based costing and job costing. It also includes calculations for ton kilometers, passenger kilometers, and profit reconciliation, along with definitions of key terms like abnormal gain, operating costing, and marginal costing. Additionally, the document outlines the treatment of abnormal loss and gain, along with the significance of break-even points and the valuation of stock in cost and financial accounts.
Uploaded by
xyz065993Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8