0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views23 pagesComputer Network (Components and Functions of A Network)
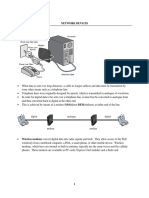
The document outlines the basic components and functions of a computer network, including transmission media (wired and wireless) and connection devices such as routers, switches, and modems. It explains the characteristics of different types of connections and the importance of network interface cards for device connectivity. Additionally, it discusses the factors influencing the choice of transmission media and the role of various devices in ensuring efficient data traffic within a network.
Uploaded by
d9bt2r5dr8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views23 pagesComputer Network (Components and Functions of A Network)
The document outlines the basic components and functions of a computer network, including transmission media (wired and wireless) and connection devices such as routers, switches, and modems. It explains the characteristics of different types of connections and the importance of network interface cards for device connectivity. Additionally, it discusses the factors influencing the choice of transmission media and the role of various devices in ensuring efficient data traffic within a network.
Uploaded by
d9bt2r5dr8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23