100% found this document useful (1 vote)
139 views11 pagesBasic Accounting
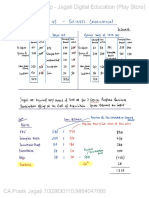
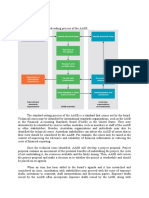
The document provides an overview of basic accounting principles, including types of accounts (Personal, Real, and Nominal), rules of debit and credit, and key definitions related to business transactions. It explains various financial statements such as the Trial Balance, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, along with concepts like assets, liabilities, capital, and different types of loans. Additionally, it distinguishes between direct and indirect expenses, detailing their implications in financial reporting.
Uploaded by
krishna.sigmaconCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
139 views11 pagesBasic Accounting
The document provides an overview of basic accounting principles, including types of accounts (Personal, Real, and Nominal), rules of debit and credit, and key definitions related to business transactions. It explains various financial statements such as the Trial Balance, Profit and Loss Account, and Balance Sheet, along with concepts like assets, liabilities, capital, and different types of loans. Additionally, it distinguishes between direct and indirect expenses, detailing their implications in financial reporting.
Uploaded by
krishna.sigmaconCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11