DEPARTMENT OF BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION-BBA (GENERAL)
Course Code: BBA 5.6 (B) Vocational
Name of the Course: Digital Marketing
Prepared By: Prof.Smitha Biji
MODULE-1
INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL MARKETING(12 HOURS)
• Introduction- Meaning and Need
• Digital Marketing platforms
• Business Email Marketing- Meaning &Importance
• E-mail Marketing platforms
• Contact Management and Segmentation Strategy
• E-mail Marketing
e-mail Deliverability
Tracking e-mails
Content & Design
Open rates, CTR & Lead Generation
• Automation Content Marketing
DIGITAL MARKETING
• Digital marketing is a broad term encompassing all marketing efforts using an
electronic device or the internet.
• It involves promoting products, services, or brands to a target audience through
various online channels and technologies.
Evolution of Digital Marketing – The Timeline
The 90s
• Archie, the first search engine, debuted in the early 1990s, heralding the birth of
search,Search Engine Optimization, quickly followed.
1
� • The first clickable web-ad banners were introduced in 1994.
• The first identifiable social media site was launched in 1997, with 3.5 million
users.
• In the 1990s, a slew of websites still in use was found, including Google and
Yahoo's web search, both of which debuted in 1998.
• Digital marketing started in India between the period 1996 – 2005.
However, the real growth of digital marketing started in 2008
The Millennial Generation
• Many new sites were launched in the 2000s, including the beginnings of
LinkedIn in 2002, Myspace and WordPress in 2003, and Facebook in 2004.
In the early 2000s, mobile text messaging marketing became increasingly
popular.
The Mobile Era
• The latter half of the decade saw increased marketing and sales, with Amazon's
e-commerce sales surpassing $10 billion. Over the next few years, mobile app
culture expanded with the introduction of WhatsApp, Instagram, and Snapchat
to the digital world.
The Present
• Today, 65% of an individual's digital media time is spent on a mobile device.
• The digital advertising industry is now valued at around $200 billion, with
Google Ad Words accounting for 96% of the company's revenue.
• With an estimated 3.1 billion online users, social networking has led the digital
marketing revolution.
• The rise of bloggers and Instagram has resulted in a $1 billion industry for
influencers, which are anticipated to grow.
• Digital marketing is expected to grow in the coming years, with many new
developments and changes in this exciting industry.
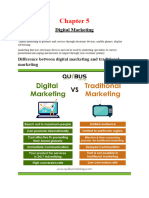
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TRADITIONAL MARKETING AND
DIGITAL MARKETING
BASIS FOR
TRADITIONAL MARKETING DIGITAL MARKETING
COMPARISON
Meaning Traditional Marketing refers to Digital Marketing implies the marketing
the marketing that uses of products and services via digital
traditional channels or media for channels, such as the internet,
marketing communication. smartphone, display ads, and other
digital medium.
Nature Static Dynamic
2
� BASIS FOR
TRADITIONAL MARKETING DIGITAL MARKETING
COMPARISON
Conversion Slow Comparatively fast
Engagement Low Comparatively high
Return on Cannot be measured easily. Can be measured easily.
Investment
Effectiveness and Less effective more expensive Less expensive more effective
expensiveness
Tracking Not possible Possible
Targeting Standardized Customized
Tweaking Not possible once the ad is Can be performed anytime, even after
placed. the ad is placed.
Reach Local Global
Results Delayed results Quick and real-time results
Interruptions Consumers cannot skip the ads, Allows the consumers to avoid or skip
as they are bound to see them. the ads which do not interest them.
Communication One-way Communication Two-way Communication
NEED OF DIGITAL MARKETING
Digital marketing plays a crucial role in today's business landscape for several reasons:
1. Online Presence: In a world where people spend significant time online, digital
marketing helps businesses establish and maintain a strong online presence. This
is essential for reaching and engaging with potential customers.
2. Global Reach: Digital marketing enables businesses to reach a global audience.
Whether a local business or a multinational corporation, the Internet allows to
expand your reach to a broader customer base.
3. Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional marketing methods like TV ads or
billboards, digital marketing is often more cost-effective. One can reach a large
audience with a smaller budget thanks to various digital marketing channels.
4. Measurable Results: Digital marketing provides detailed analytics and metrics to
track the performance of the campaigns. This means one can measure the ROI of
the marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions.
5. Targeted Advertising: With digital marketing, a business can precisely target
their audience based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and other criteria.
This increases the chances of reaching the right people with the message.
6. Personalization: Digital marketing allows businesses to create personalized
content and offers for their audience. Personalization can significantly enhance the
customer experience and improve conversion rates.
7. Instant Communication: Social media, email, and other digital channels enable
real-time communication with customers. This allows businesses to provide
immediate responses to inquiries and build stronger customer relationships.
3
� 8. Flexibility: Digital marketing campaigns can be adjusted and optimized on the fly.
If one notice that a particular strategy isn't working, one can make changes quickly
to improve results.
9. E-commerce and Online Sales: Digital marketing is crucial for e-commerce
businesses, allowing them to promote products and drive online sales. It's also
essential for businesses with online booking systems or appointment scheduling.
10. Brand Building: Consistent digital marketing efforts can help build and
strengthen the brand. Through storytelling and customer engagement, one can
create a memorable brand identity.
11. Social Proof: Reviews and testimonials on various online platforms are integral to
building trust. Digital marketing can help the business showcase positive feedback
and credibility.
12. Data Insights: Digital marketing provides valuable insights into customer
behavior, preferences, and trends. This data can inform the overall business
strategy.
13. Adaptation to Consumer Behavior: As consumer behavior evolves and more
people turn to online research and shopping, digital marketing allows businesses
to adapt and stay relevant.
BUSINESS EMAIL MARKETING
• Email marketing is to send targeted messages and promotional content to new or
future customers by email.
• It is a powerful digital marketing strategy that allows businesses to communicate
directly with their audience, build strong relationships with customers, nurture
leads, and sell their products and services.
ADVANTAGES/IMPORTANCE OF EMAIL MARKETING
• People check their email a lot, up to 20 times a day so reach and visibility is high.
• Even when sent in bulk, emails can be personalized and segmented to help
individuals feel like you’re talking just to them.
• Email is easy to automate and scale.
• Email has an extremely high ROI (return on investment).
• It’s affordable
TYPES OF EMAIL MARKETING CAMPAIGNS
1. Newsletters: Regular updates sent to subscribers with news, articles, and content
related to the brand or industry. These help to maintain a connection with
subscribers and provide value beyond product promotion.
2. Welcome Messages: The first email(s) sent to new subscribers or customers,
introducing them to the brand, setting expectations, and often including a
welcome offer or call-to-action.
4
� 3. Anniversary or Birthday Messages: Personalized emails sent on special dates,
like birthdays or customer anniversaries, to show appreciation and encourage
engagement, often with a special offer.
4. Limited Time Offers: Emails promoting special deals that are available for a short
period. These create a sense of urgency and encourage quick action.
5. Abandoned Cart Emails: Sent to customers who added items to their online
shopping cart but didn't complete the purchase. These emails remind them of the
items and may include incentives to complete the transaction.
E-MAIL MARKETING PLATFORMS
An email marketing platform is software or an online service designed to help
businesses and marketers create, manage, and analyze email marketing campaigns.
These platforms offer tools and features that streamline the process of sending emails to
large lists of subscribers, enabling businesses to communicate effectively, nurture leads,
and promote their products or services.
Key Features of Email Marketing Platforms:
1. Email Creation and Design
Most platforms offer drag-and-drop editors and customizable templates,
allowing users to create professional and visually appealing emails without
needing design or coding skills.
2. List Management and Segmentation
These tools help manage subscriber lists, allowing businesses to segment their
audience based on demographics, behaviors, or other criteria. This enables
personalized marketing by sending targeted emails to specific groups.
3. Automation
Many platforms provide automation capabilities, such as drip campaigns,
autoresponders, and trigger-based emails (e.g., welcome emails, abandoned cart
reminders). Automation saves time and ensures timely, relevant messages are
sent to customers.
4. Personalization
Email marketing platforms allow users to personalize emails with subscriber
names, preferences, and other data. Personalization can increase engagement and
make emails feel more relevant to recipients.
5. Analytics and Reporting
Most platforms offer detailed metrics, such as open rates, click-through rates,
conversion rates, and unsubscribe rates. Analytics help businesses track the
effectiveness of their campaigns and make data-driven decisions to improve
performance.
Popular Email Marketing Platforms
Some popular email marketing platforms include:
5
� Mailchimp: Known for its ease of use and comprehensive features, suitable for
small to medium businesses.
Constant Contact: Offers a range of templates and list management tools, along
with social media integration.
HubSpot: Part of a larger marketing suite, suitable for businesses looking for a full
CRM with email marketing.
SendinBlue: Known for its automation tools and SMS marketing capabilities.
ActiveCampaign: Popular for its advanced automation and CRM integration,
often used by more advanced marketers.
CONTACT MANAGEMENT AND SEGMENTATION STRATEGY
A contact management and segmentation strategy is a way to organize and store
customer information, and track business interactions.
The goal is to keep important contact information organized for easy access.
COMPONENTS
1. Collect and Organize Contact Information:
• Gather contact information from various sources, such as sign-up forms,
purchases, and events.
2. Clean and Update the Contact List:
• Regularly clean the contact list to remove duplicates, invalid emails, and
unsubscribed contacts.
3. Segment the Contacts:
Divide the contacts into segments based on specific criteria that matter to the business.
Common segmentation criteria include:
1. Demographics (age, gender, location, etc.)
2. Behavior (purchase history, website visits, email engagement)
3. Preferences (product interests, content preferences)
4. Lifecycle stage (prospects, customers, loyal customers)
4. Define Personas:
Create buyer personas based on the segments. Personas are fictional representations of
your ideal customers, and they help to tailor the messaging to different audience types.
5. Craft Targeted Message:
1. Develop content and messaging tailored to each segment or persona.
2. Consider the unique needs, challenges, and interests of each group when
creating the content.
6
�6. Automate Communication:
1. Use marketing automation tools to schedule and send targeted emails or
messages to the right segments at the right time.
2. Implement personalized recommendations and dynamic content to
increase engagement.
7. A/B Testing(split testing or bucket testing)
Continuously test different elements of your communication (subject lines, content, calls
to action) to optimize engagement and conversion rates for each segment.
8.Monitor and Analyze Results:
• Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as open rates, click-through rates,
conversion rates, and revenue generated from each segment.
9. Iterate and Improve:
• Based on the results and insights, refine your segmentation strategy and
messaging to improve performance continually.
• Keep your contact list up-to-date with ongoing data management.
10. Compliance and Privacy:
• Ensure that your contact management strategy complies with data protection laws
and respects individuals' privacy rights.
• "Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act)" which mandates businesses to
collect, store, and process user data with transparency, obtaining explicit consent
from users, and ensuring robust data security practices, all while allowing
individuals control over their personal information; essentially requiring
marketers to prioritize user privacy in their campaigns and operations.
• The CAN-SPAM Act, a law that sets the rules for commercial email, establishes
requirements for commercial messages, gives recipients the right to have you stop
emailing them, and spells out tough penalties for violations.
E-MAIL DELIVERABILITY
• Email deliverability is the ability of an email message to arrive in the
recipient's main email inbox. Email deliverability is often measured as a
percentage of emails accepted by the internet service provider.
FACTORS AFFECTING
1. SENDER REPUTATION:
IP Reputation: The reputation of the IP address from which the email is sent is crucial. If
the IP address is associated with spammy behavior, emails are more likely to be flagged
as spam. IP address might look like 192.0.2.1
7
�Domain Reputation: Similar to IP reputation, the sending domain’s reputation is
important. If a domain has a history of sending spam, it can affect deliverability. (@.com
or .in).
2. Content and Engagement:
Relevant Content: Emails with relevant and valuable content are less likely to be marked
as spam. Avoid using deceptive subject lines and misleading content.
3. List Quality:
Permission-based Lists: Sending emails to explicitly opted-in recipients is crucial.
Maintaining a clean list.
4..Frequency and Consistency:
Sending Frequency: Sending too many emails in a short period or irregular sending
patterns can trigger spam filters. Consistent, moderate sending is often more favorable.
Bounce Rates: High bounce rates (undelivered emails) can negatively impact reputation.
Keep email lists clean by removing invalid addresses.
TRACKING EMAILS
Email tracking is a method for monitoring if an email is read by the recipient. It can also
include tracking when the email was received or opened.
• Open Tracking
• Click Tracking
• Bounce Tracking
• Unsubscribe tracking
• Conversion Tracking(Specific to sign up download a resource)
CONTENT & DESIGN
How to create effective and unique e-mail content
1. Understand Audience
2. Set Clear Goals
3. Compelling subject lines
4. Personalization
5. Clear and concise content
6. Compelling Visuals
8
� 7. Value Preposition- Why recipient should open & read the email?
8. Engaging call to action- “Shop Now”, “Learn More”, “Get Started”, “Download Now”
9. Mobile Responsiveness
OPEN RATES
Open rate is a metric used in email marketing to measure the percentage of recipients
who open a message.
It's calculated by dividing the number of people who open the email by the number of
people who received it.
TIPS FOR INCREASING EMAIL OPEN RATES:
• Make subject lines stand out
• Use emojis in subject lines
• Use a fun, conversational tone
• Send emails at the most appropriate time
• Make emails mobile-friendly
Low open rates could be caused by:
• Poor-quality email list.
• Email list that's too old.
CLICK-THROUGH RATE
CLICK-THROUGH RATE (CTR) is the percentage of individuals viewing a web page
who view and then click on a specific advertisement that appears on that page.
• Click-through rates measure an ad’s success in capturing users' attention.
• The higher the click-through rate, the more successful the ad has been in
generating interest.
CLICK-THROUGH RATES IN EMAIL MARKETING
• Click-through rates for emails are calculated in much the same way, but instead of
an advertisement being served and clicked on a website, you would consider the
percentage of times an email recipient clicks on one or more links in an email to
be taken to the sender's website or other destination.
• It is more easily understood as the total number of clicks an email has generated
for its sender. Email marketers may pair click-through rates with open rates,
9
� bounce rates, and other measurements to calculate the effectiveness of their
campaigns.
LEAD GENERATION
Lead generation in digital marketing is the process of attracting and capturing the
interest of potential customers (leads) in order to build a list of contacts who may
eventually purchase a product or service. It’s a key step in a digital marketing strategy,
as it helps businesses build relationships with prospects, nurture them, and guide them
down the sales funnel.
Key Elements of Lead Generation in Digital Marketing:
1. Landing Pages: A landing page is a dedicated webpage designed to capture lead
information through a form. These pages are highly focused, with a single goal:
convincing visitors to provide their contact information in exchange for the lead
magnet. They usually have persuasive copy, a clear call-to-action (CTA), and
minimal distractions.
2. Forms and CTAs: Forms are used to collect lead information (name, email, job
title, etc.), while CTAs (call-to-action buttons or links) encourage visitors to take a
specific action, such as signing up for a newsletter or downloading a free resource.
Effective forms and CTAs are crucial for converting website visitors into leads.
3. Content Marketing: Content marketing involves creating and sharing valuable
content, like blog posts, videos, and infographics, to attract potential leads. High-
quality content helps establish a business as a trusted authority and provides
opportunities to capture leads, often through CTAs within the content.
4. Social Media Marketing: Social media platforms are powerful tools for lead
generation. Businesses can promote lead magnets, engage with potential
customers, and direct traffic to landing pages. Features like "Swipe Up" on
Instagram stories or "Lead Gen Forms" on LinkedIn are also popular for capturing
leads.
5. Email Marketing: Email marketing helps nurture leads by providing them with
valuable content, updates, and offers over time. Welcome emails, newsletters, and
drip campaigns are common email types used to engage leads and guide them
toward conversion.
OPT IN LIST
An opt-in list is a list of people who have requested to receive communications from a
specific organization or website.
They are lists of contacts who have voluntarily given their email address. The recipients
are aware that they are being added to the list and agree to receive digital communication
from the sender.
There are two types of opt-in lists:
• Single opt-in: Users only need to subscribe once to start receiving emails.
• Double opt-in: Users must subscribe and then confirm their email address
through a link.
10
�CONTENT MARKETING
• Content marketing is a marketing strategy involving the creation and sharing of
relevant materials, such as articles, videos, social media posts, and emails, to
attract and engage audiences, establish expertise, promote brand awareness, and
drive sales.
GENERATING CONTENT IDEAS AND LONG-TERM CONTENT STRATEGY
Generating Content Ideas
Audience Research: Identify audience needs, pain points, and interests.
Competitor Analysis: Review competitor content to spot gaps and opportunities.
Keyword Research: do thorough keyword research to find trending topics.
Social Media Listening: Monitor social media for trending topics and discussions.
Customer Feedback: Gather insights from reviews, surveys, and customer
service queries.
Industry Trends: Follow industry news and updates to stay relevant.
Content Repurposing: Update and repurpose high-performing older content.
Brainstorm with Teams: Collaborate with sales, support, and marketing teams
for fresh ideas.
Content Gaps Analysis: Use analytics to find topics your audience searches for
but aren't covered in your content.
Developing a Long-Term Content Strategy
Set Clear Goals: Define objectives (brand awareness, lead generation, customer
engagement).
Audience Persona Development: Create detailed profiles of your target
audience.
Content Pillars: Identify core themes that align with your brand and audience
interests.
Content Calendar: Plan and schedule content in advance to maintain consistency.
Diverse Content Formats: Incorporate blogs, videos, infographics, podcasts, etc.,
to engage different audience types.
Content Distribution Plan: Decide on platforms (blog, social media, email) to
reach your audience effectively.
Content Repurposing Strategy: Create adaptable content that can be used across
various formats and channels.
Engagement and Community Building: Focus on creating interactive content
and building a community.
Measure and Adjust: Use analytics to track performance, and regularly update
the strategy based on insights.
11
�PROMOTING THE CONTENT IN DIGITAL MARKETING.
Promoting content in digital marketing involves using various tactics to increase
visibility, engagement, and reach. Here are key strategies:
1. Social Media Marketing: Share content across social platforms (Facebook,
Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram) to engage followers and attract new audiences. Use
hashtags, and schedule posts for maximum reach.
2. Email Marketing: Send content to subscribers through newsletters or targeted
email campaigns. Segment the audience to ensure relevant content reaches the
right people.
3. Paid Advertising: Use paid ads on platforms like Google Ads, Facebook, and
Instagram to boost content visibility. Sponsored posts and pay-per-click (PPC) ads
can help reach a larger or more targeted audience.
4. Influencer Marketing: Collaborate with influencers in your niche to share
content with their followers. This can boost credibility and expand reach to a
broader audience.
5. Guest Blogging: Write articles for other blogs or sites in your niche and include
links to your content. This increases brand visibility and drives referral traffic.
6. Remarketing
Use remarketing ads to re-engage users who have previously interacted with your
content or website, encouraging them to return and explore further.
7. Repurposing Content
Adapt content into different formats, such as videos, infographics, or podcasts, to
reach audiences across different platforms.
12