0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views27 pagesEcom Notes
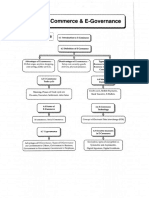
The document provides a comprehensive overview of e-commerce, covering its meaning, nature, advantages, disadvantages, types, models, and challenges. It also discusses the growth of e-commerce in India, its transition stages, readiness indicators, and security issues related to online transactions. Additionally, it highlights the applications of e-commerce across various industries such as retail, banking, travel, education, healthcare, and entertainment.
Uploaded by
preritverma5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views27 pagesEcom Notes
The document provides a comprehensive overview of e-commerce, covering its meaning, nature, advantages, disadvantages, types, models, and challenges. It also discusses the growth of e-commerce in India, its transition stages, readiness indicators, and security issues related to online transactions. Additionally, it highlights the applications of e-commerce across various industries such as retail, banking, travel, education, healthcare, and entertainment.
Uploaded by
preritverma5Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 27