0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views8 pagesMaths Formulas
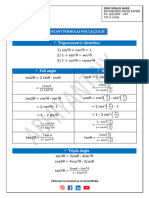
The document provides a comprehensive overview of differentiation and integration rules in calculus, including derivatives of various functions such as polynomials, logarithmic, exponential, and trigonometric functions. It also covers the addition, product, quotient, and chain rules for derivatives, as well as logarithmic differentiation and the derivatives of inverse functions. Additionally, the document lists several indefinite integrals with their respective results, offering a valuable reference for calculus students.
Uploaded by
premchandcheggCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views8 pagesMaths Formulas
The document provides a comprehensive overview of differentiation and integration rules in calculus, including derivatives of various functions such as polynomials, logarithmic, exponential, and trigonometric functions. It also covers the addition, product, quotient, and chain rules for derivatives, as well as logarithmic differentiation and the derivatives of inverse functions. Additionally, the document lists several indefinite integrals with their respective results, offering a valuable reference for calculus students.
Uploaded by
premchandcheggCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8