0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pagePiecewise Functions
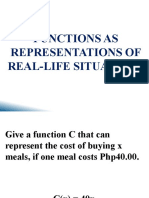
The document discusses piecewise functions through various examples, including cost functions for meals, transportation fares, and catering services. It illustrates how to represent different scenarios with distinct formulas based on specific conditions. Additionally, it explains the concept of piecewise functions as those built from multiple pieces over varying intervals of inputs.
Uploaded by
mickelatatoy466Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pagePiecewise Functions
The document discusses piecewise functions through various examples, including cost functions for meals, transportation fares, and catering services. It illustrates how to represent different scenarios with distinct formulas based on specific conditions. Additionally, it explains the concept of piecewise functions as those built from multiple pieces over varying intervals of inputs.
Uploaded by
mickelatatoy466Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 1