0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views11 pagesM3.3 Microcontroller 8051
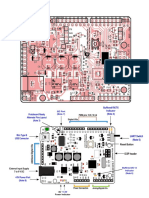
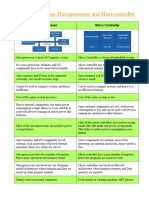
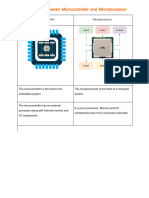
Microcontrollers integrate a microprocessor with memory and input/output interfaces on a single chip, making them suitable for control-oriented applications with low power consumption. In contrast, microprocessors require external components for memory and I/O, making them more powerful but less efficient for compact systems. Microcontrollers are widely used in embedded systems across various applications including home appliances, office equipment, and automotive systems.
Uploaded by
22210023 MAHADIK PRASAD AMARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views11 pagesM3.3 Microcontroller 8051
Microcontrollers integrate a microprocessor with memory and input/output interfaces on a single chip, making them suitable for control-oriented applications with low power consumption. In contrast, microprocessors require external components for memory and I/O, making them more powerful but less efficient for compact systems. Microcontrollers are widely used in embedded systems across various applications including home appliances, office equipment, and automotive systems.
Uploaded by
22210023 MAHADIK PRASAD AMARCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 11