0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views5 pagesData Models
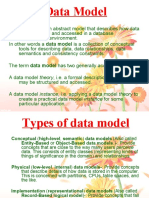
Data models in Database Management Systems (DBMS) summarize database descriptions and aid in database creation. They are classified into three types: Conceptual, Representational, and Physical Data Models, each serving different purposes from high-level design to practical implementation. While data modeling enhances data organization and integrity, it can also be complex and requires knowledge of SQL for effective use.
Uploaded by
kalai vendhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views5 pagesData Models
Data models in Database Management Systems (DBMS) summarize database descriptions and aid in database creation. They are classified into three types: Conceptual, Representational, and Physical Data Models, each serving different purposes from high-level design to practical implementation. While data modeling enhances data organization and integrity, it can also be complex and requires knowledge of SQL for effective use.
Uploaded by
kalai vendhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5