0% found this document useful (0 votes)
467 views6 pagesLayout Interview Questions and Answers
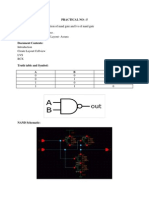
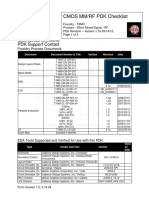
The document presents the top 20 interview questions and answers related to VLSI layout, covering essential concepts such as DRC, LVS, antenna effect, and latch-up prevention. It discusses various layout elements like vias, dummy fills, guard rings, and decap cells, emphasizing their significance in ensuring manufacturability and reliability. Additionally, it outlines the typical steps involved in physical verification to confirm design correctness before fabrication.
Uploaded by
Dhanvi GCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
467 views6 pagesLayout Interview Questions and Answers
The document presents the top 20 interview questions and answers related to VLSI layout, covering essential concepts such as DRC, LVS, antenna effect, and latch-up prevention. It discusses various layout elements like vias, dummy fills, guard rings, and decap cells, emphasizing their significance in ensuring manufacturability and reliability. Additionally, it outlines the typical steps involved in physical verification to confirm design correctness before fabrication.
Uploaded by
Dhanvi GCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6