0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesPersonal Development Notes
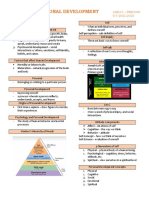
The document discusses personal development, focusing on human development's three aspects: physical, cognitive, and psychosocial. It outlines factors influencing development, such as heredity, environment, and maturation, and introduces concepts like self-concept and self-esteem. Additionally, it highlights the stages of human development, the importance of self-knowledge, and the role of positive psychology in fostering personal growth.
Uploaded by
Christina AlagadanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesPersonal Development Notes
The document discusses personal development, focusing on human development's three aspects: physical, cognitive, and psychosocial. It outlines factors influencing development, such as heredity, environment, and maturation, and introduces concepts like self-concept and self-esteem. Additionally, it highlights the stages of human development, the importance of self-knowledge, and the role of positive psychology in fostering personal growth.
Uploaded by
Christina AlagadanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8