0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views42 pagesC01-Basic Handling - V2017R4
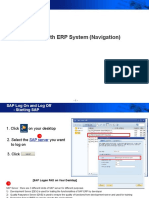
The document provides a comprehensive guide on basic handling of the abas ERP system, covering login procedures, command overview, data types, and screen functionalities. It explains how to customize command overviews, select data records using various methods, and utilize keyboard shortcuts for efficient operation. Additionally, it details the structure of database screens and the use of selection criteria for data retrieval.
Uploaded by
Joao AndarilhoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views42 pagesC01-Basic Handling - V2017R4
The document provides a comprehensive guide on basic handling of the abas ERP system, covering login procedures, command overview, data types, and screen functionalities. It explains how to customize command overviews, select data records using various methods, and utilize keyboard shortcuts for efficient operation. Additionally, it details the structure of database screens and the use of selection criteria for data retrieval.
Uploaded by
Joao AndarilhoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 42