TAKE ACTION
Unit 3 Lesson 2
AGENDA
1) Formal and informal language review
2) Analysing target audiences
1) Creating a brochure
1
� VOCABULARY
consensus (n) opinion that everyone in a group agrees with
emission (n) something that has been released into the world e.g gas or light
greenhouse (n) building with a roof and sides made of glass, for growing plants
industrial (adj) something related to a manufacturing business
combustion (n) burning
sustainable (adj) ability or possibility of maintaining or supporting something for a long time
architecture (n) the art of designing buildings
to green (v) to make something or someone less harmful to the environment
voyage (n) long journey, usually across the ocean or space
to discard (v) to throw away
VOCABULARY
A) combustion (n) 1) building with a roof and sides made of glass, for growing plants
B) architecture (n) 2) burning
C) voyage (n) 3) opinion that everyone in a group agrees with
D) industrial (adj) 4) the art of designing buildings
E) to green (v) 5) ability or possibility of maintaining or supporting something for a long time
F) consensus (n) 6) to throw away
G) to discard (v) 7) something that has been released into the world e.g gas or light
H) emission (n) 8) to make something or someone less harmful to the environment
I) sustainable (adj) 9) something related to a manufacturing business
J) greenhouse (n) 10) long journey, usually across the ocean or space
2
� VOCABULARY
1) J
2) A
3) F
4) B
5) I
6) G
7) H
8) E
9) D
10) C
SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
A colon can be used to introduce a list, for example:
The average household bin contains: paper and
card, organic matter, metal, glass, etc.
Textbook page 138
3
� SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
1.) Use a colon and a list to complete these two
sentences.
a) The ingredients for a cheese and pickle sandwich
are...
b) My favourite things in the whole world are...
Textbook page 138
SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
1.) Use a colon and a list to complete these two
sentences.
a) The ingredients for a cheese and pickle sandwich
are: bread, cheese, lettuce, mayo, and pickles.
b) My favourite things in the whole world are: dogs,
movies, food, and flowers.
Textbook page 138
4
� SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
A semi-colon is sometimes used to join two clauses in
a sentence, taking the place of a conjunction like and
or but. For example:
I love listening to loud music but the neighbours hate
it.
I love listening to loud music; the neighbours hate it.
Textbook page 138
SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
2.) Rewrite these sentences using a semi-colon:
a) My sister is really good at cooking and she makes
delicious cakes.
b) My dog's breath smells but my brother smells
worse.
Textbook page 138
5
� SHARPEN YOUR SKILLS
2.) Rewrite these sentences using a semi-colon:
a) My sister is really good at cooking; she makes
delicious cakes.
b) My dog's breath smells; my brother smells worse.
Textbook page 138
FORMAL & INFORMAL LANGUAGE
QUICK, teach your partner!
There are three prompts on
the next slide that you will use
to review with your partner.
6
� FORMAL & INFORMAL LANGUAGE
1.) What is the difference
between formal and
informal language?
2.) When do you use formal
language?
3.) When do you use
informal language?
FORMAL & INFORMAL LANGUAGE
Formal language features:
• no contractions
• complex sentences
Informal language features:
• contractions
• slang
• simple words
7
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
These three speakers are talking about recycling.
1.) What situation could each of them be
in?
2.) Who do you think they are talking to?
3.) Which uses the most formal language?
4.) Which uses the most informal
language?
Textbook page 140 activity 1
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
These three speakers are talking about recycling.
A) Formal: perhaps from a speech or
a similarly formal occasion.
Textbook page 140 activity 1
8
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
These three speakers are talking about recycling.
B) Informal: perhaps aimed at a
younger audience.
Textbook page 140 activity 1
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
These three speakers are talking about recycling.
C) More formal than B, but still
informal: aimed at a wider audience.
Textbook page 140 activity 1
9
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Many texts are written to appeal
to a specific audience: the target
audience.
This may be people of a particular
age group, or with a particular
interest. Let's look at some
magazine covers.
Textbook page 140 activity 2
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
1.) For each one, describe the
target audience. Who would read
this magazine?
2.) Would you expect the language
used in these magazines to be
more formal or more informal?
Textbook page 140 activity 2
10
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) People interested in environmental
issues, science, and exploration in Asia
B) Children who are picky eaters
C) Backpackers who want to travel Asia
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) People interested in environmental
issues, science, and exploration in Asia
B) Children who are picky eaters
C) Backpackers who want to travel Asia
11
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
2.) Would you expect the language used
in this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
2.) Would you expect the language used
in this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
More formal
12
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) Women who like plants
B) People interested in sustainable
architecture
C) Business men who want a new
workplace
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) Women who like plants
B) People interested in sustainable
architecture
C) Business men who want a new
workplace
13
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
More formal
14
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) Children interested in space
B) Elderly people
C) Astronauts
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) Children interested in space
B) Elderly people
C) Astronauts
15
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
More informal
16
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) People that like the colour pink
B) Elderly people
C) People who like to garden
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Who is the target audience?
A) People that like the colour pink
B) Elderly people
C) People who like to garden
17
�AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
AIMING AT A TARGET AUDIENCE
Would you expect the language used in
this magazine to be more formal or
more informal?
More formal
18
� FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Sometimes, we use
names in different ways
in different situations.
We also wear different
clothes for different
occasions--and it's
important to get the
right clothes for the
right occasion.
FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
The same is true of the
words we use. Some
are appropriate to a
formal situation, some
are more suited to an
informal situation.
19
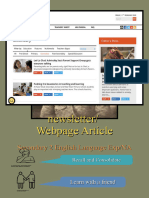
� FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
But even the way a
website looks can be
formal or informal.
A) Which website is
formal?
B) Which website is
informal?
FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
• Bright colours that grab your • Dark, bold, serious colours
attention • Men in suits that look
• Animated art style and professional
characters • Advertises legal advice and
• Advertises games and shows law services
20
� FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Let's look at two
more examples from
the textbook.
Textbook page 141 activity 3
FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Textbook page 141 activity 3
21
�FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Which features best fit the web page?
1.) simple language
2.) complicated language
3.) short sentences
4.) long sentences
5.) informal
6.) formal
Textbook page 141 activity 3
FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Which features best fit the web page?
1.) simple language
2.) complicated language
3.) short sentences
4.) long sentences
5.) informal
6.) formal
Textbook page 141 activity 3
22
�FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Which features best fit the web page?
1.) simple language
2.) complicated language
3.) short sentences
4.) long sentences
5.) informal
6.) formal
Textbook page 141 activity 3
FORMAL VS INFORMAL STYLE
Which features best fit the web page?
1.) simple language
2.) complicated language
3.) short sentences
4.) long sentences
5.) informal
6.) formal
Textbook page 141 activity 3
23
� THE THREE Rs
Do you remember what The Three Rs are from last week?
THE THREE Rs
REDUCE
REUSE
RECYCLE
24
� REDUCE
Consuming and buying
LESS.
For example: instead of
buying two small water
bottles, buy one big one.
REUSE
Reuse things and give
them the greatest possible
use before discarding
them.
For example: refilling a
water bottle instead of
throwing it away.
25
� RECYCLE
Recycle items whenever
possible so they can
become something new.
For example: paper can
be recycled into a box.
CREATE A BROCHURE
Work in groups of 3-4 to
create an informational
brochure for your
school!
26
� CREATE A BROCHURE
Your brochure must:
• teach your fellow students
about The Three Rs and what
each letter means.
• include ideas of how students
can make your school become
more environmentally friendly.
IT'S TIME TO WORK
1) Cover page (title and decorations)
2) The Three Rs introduction page
3) Reduce page • You must use your own words to teach your
4) Reuse page fellow students about The Three R's and what
each letter means.
5) Recycle page
• include ideas of how students can make your
school become more environmentally
friendly.
27
� VOCABULARY TASK
Complete the gaps in your WB with words from the list.
1. My neighbour grows strawberries inside of her ____ .
2. It took a long time for my group to come to a ____ about our
project.
3. I try to buy clothing that comes from a ____ source.
4. Rome is famous for its ____.
5. He wrote about his ____ across the sea.
VOCABULARY TASK
Complete the gaps in your WB with words from the list.
1. My neighbour grows strawberries inside of her greenhouse.
2. It took a long time for my group to come to a consensus
about our project.
3. I try to buy clothing that comes from a sustainable source.
4. Rome is famous for its architecture.
5. He wrote about his voyage across the sea.
28
� PLENARY
1.) When would you use semi-formal language?
2.) Why would a magazine use informal language?
3.) What is one way a website can be informal?
29