Java Serialization and Deserialization
Serialization
Definition:
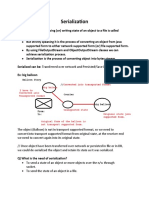
To serialize an object means to convert its state to a byte stream so that the byte stream
can be reverted back into a copy of the object.
A Java object is serializable if its class or any of its superclasses implements either the
java. io. Serializable interface or its subinterface, java.
Serialization is the conversion of an object to a series of bytes, so that the object can be
easily saved to persistent storage or streamed across a communication link. The byte
stream can then be deserialized - converted into a replica of the original object.
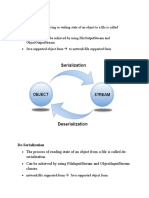
Serialization is a process of converting an object into a sequence of bytes which can be
persisted to a disk or database or can be sent through streams.
The reverse process of creating object from sequence of bytes is called deserialization.
A class must implement Serializable interface present in java.io package in order to
serialize its object successfully.
Serializable is a marker interface that adds serializable behaviour to the class
implementing it.
Java provides Serializable API encapsulated under java.io package for serializing and
deserializing objects which include,
java.io.serializable
java.io.Externalizable
ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream
Java Marker interface:
Marker Interface is a special interface in Java without any field and method.
Marker interface is used to inform compiler that the class implementing it has some
special behaviour or meaning.
Some example of Marker interface are,
java.io.serializable
1
� java.lang.Cloneable
java.rmi.Remote
java.util.RandomAccess
All these interfaces does not have any method and field.
They only add special behavior to the classes implementing them.
However marker interfaces have been deprecated since Java 5, they were replaced
by Annotations.
Annotations are used in place of Marker Interface that play the exact same role as marker
interfaces did before.
To implement serialization and deserialization, Java provides two classes
ObjectOutputStream and ObjectInputStream.
ObjectOutputStream class:
It is used to write object states to the file. An object that implements java.io.Serializable
interface can be written to strams.
It provides various methods to perform serialization.
Methods:
Writes the specified object to the object to the objectOutputStream.
public final void writeObject(object x) throws IOException{ }
Flushes the current output stream.
public void flush ( ) throws IOException{ }
Closes the current output stream.
public void close ( ) throws IOException{ }
ObjectInputStream class:
An ObjectInputStream deserializes objects and primitive data written using an
ObjectOutputStream.
2
� writeObject() and readObject() Methods
The writeObject() method of ObjectOutputStream class serializes an object and send it to
the output stream.
The readObject() method of ObjectInputStream class references object out of stream and
deserialize it.
public final Object readObject() throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException
while serializing if you do not want any field to be part of object state then declare
it either static or transient based on your need and it will not be included during
java serialization process.
3
�Example: Serializing an Object in Java
In this example, we have a class that implements Serializable interface to make its object
serialized.
import java.io.*;
class Studentinfo implements Serializable {
String name;
int rid;
static String contact;
Studentinfo(String n, int r, String c) {
this.name = n;
this.rid = r;
this.contact = c; } }
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Studentinfo si = new Studentinfo("Abhi", 104, "110044");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("student.txt");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(si);
oos.flush();
oos.close(); }
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e); } } }
Object of Studentinfo class is serialized using writeObject() method and written
to student.txt file.
4
� Deserialization
Definition:
Deserialization is the process of reconstructing the object from the serialized state.
It is the reverse operation of serialization.
ObjectInputStream class:
An ObjectInputStream deserialization objects and primitive data written using an
ObjectInputStream.
Methods:
Reads an object from the input stream.
public final void readObject(object x) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{ }
Closes ObjectInputStream.
public void close( ) throws IOException{ }
5
�Example: Deserialization of Object in Java
To deserialize the object, we are using ObjectInputStream class that will read the object from the
specified file. See the below example.
import java.io.*;
class Studentinfo implements Serializable {
String name;
int rid;
static String contact;
Studentinfo(String n, int r, String c) {
this.name = n;
this.rid = r;
this.contact = c; } }
class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Studentinfo si=null ;
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/filepath/student.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
si = (Studentinfo)ois.readObject(); }
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(si.name);
System.out. println(si.rid);
System.out.println(si.contact); } }
6
� Output:
Abhi
104
Null
Contact field is null because, it was marked as static and as we have discussed earlier
static fields does not get serialized.
NOTE: Static members are never serialized because they are connected to class not object of
class.
transient Keyword:
While serializing an object, if we don't want certain data member of the object to be
serialized we can mention it transient.
transient keyword will prevent that data member from being serialized.
class studentinfo implements Serializable
{
String name;
transient int rid;
static String contact;
}
Making a data member transient will prevent its serialization.
In this example rid will not be serialized because it is transient, and contact will also
remain unserialized because it is static.