0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesAdvanced Database Systems Lecture 1
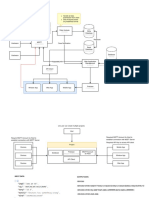
The document serves as a study guide for Advanced Database Systems, covering key concepts such as Database Management Systems (DBMS), logical vs. physical design, centralized vs. distributed architectures, and types of NoSQL databases. It also outlines the components of a database engine, the purpose of a buffer manager, normalization, ACID properties, and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in database security. Additionally, it includes a glossary of key terms relevant to database systems.
Uploaded by
silenamarshallvaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesAdvanced Database Systems Lecture 1
The document serves as a study guide for Advanced Database Systems, covering key concepts such as Database Management Systems (DBMS), logical vs. physical design, centralized vs. distributed architectures, and types of NoSQL databases. It also outlines the components of a database engine, the purpose of a buffer manager, normalization, ACID properties, and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in database security. Additionally, it includes a glossary of key terms relevant to database systems.
Uploaded by
silenamarshallvaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4