0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views22 pagesESD-CortexM3 Data Processing Instruction
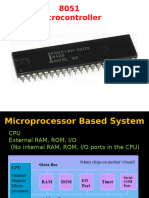
The document provides an overview of Embedded Systems Design, covering components, characteristics, and ARM architecture, specifically focusing on Cortex-M3. It details various data processing instructions, including arithmetic, logical, and bit manipulation operations, as well as real-time operating systems (RTOS) concepts. The content is aimed at students in the Department of EEE at Amrita School of Engineering, emphasizing practical applications and theoretical foundations in embedded systems.
Uploaded by
fyprject05Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views22 pagesESD-CortexM3 Data Processing Instruction
The document provides an overview of Embedded Systems Design, covering components, characteristics, and ARM architecture, specifically focusing on Cortex-M3. It details various data processing instructions, including arithmetic, logical, and bit manipulation operations, as well as real-time operating systems (RTOS) concepts. The content is aimed at students in the Department of EEE at Amrita School of Engineering, emphasizing practical applications and theoretical foundations in embedded systems.
Uploaded by
fyprject05Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 22