HO CHI MINH CITY UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY HO CHI MINH CITY
FACULTY OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
MACHINE ELEMENT
INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT REPORT
Lecturer: Dr. Phạm Minh Tuấn
Full Name: Nguyễn Phúc Khang
Student ID: 2352485
1
�Contents
1. Project requirements ................................................................................................... 3
2. Electric motor selection and transmission ratio distribution ...................................... 3
2.1. Selecting efficiency of transmission systems: ....................................................... 3
2.2. Selecting transmission ratio: ................................................................................. 3
2.3. Power, speed and torque calculations .................................................................. 4
3. Design of bevel gear drive in speed reducer ................................................................ 5
3.1. Working life and allowable stress ......................................................................... 5
3.2. Geometric calculations ......................................................................................... 6
3.3. Kinematics and dynamics ..................................................................................... 7
3.4. Verification for contact stress ............................................................................... 7
4. Design of roller chain drive .......................................................................................... 8
4.1. Choosing number of sprocket teeth Z .................................................................. 8
4.2. Calculating pitch pc ............................................................................................... 8
4.3. Preliminary geometric calculations ...................................................................... 9
4.4. Kinematics and dynamics ................................................................................... 10
4.5. Verification .......................................................................................................... 10
4.6. Dimensions of sprockets: .................................................................................... 11
5. Design of shafts in speed reducer .............................................................................. 12
5.1. Shaft 1 ................................................................................................................. 12
5.2. Shaft 2 ................................................................................................................. 14
6. Selecting bearings for shafts ...................................................................................... 17
6.1. Pair 1 (shaft 1) ..................................................................................................... 17
6.2. Pair 2 (shaft 2) ..................................................................................................... 18
2
� 1. Project requirements
• Power of blender' shaft, P = 5 kw
• Rotation speed of blender' shaft, n = 130 rpm
• Working life: L = 3 years
• Allowable transmission error: ± 5%
• Operating conditions: one-direction working, light-impact loading, 2-shift operation
(8 hours/shift) and 300 days/year
2. Electric motor selection and transmission ratio distribution
2.1. Selecting efficiency of transmission systems:
gear = 0.97
chain = 0.95 bearing = 0.99 coupling = 1
System efficiency: sys = gear chain 2bearing coupling
= 0.97 0.95 0.992 1 = 0.9
2.2. Selecting transmission ratio:
u gear = 3.6
, uchain = 2.04
3
� 2.3. Power, speed and torque calculations
PIII 5
Required power of motor: Prequired = = = 5.55
• 0.9 0.9 Kw
→ Selected motor:
Motor Power kW n (rpm)
DK 62-6 7 960
• Speed distribution for each shaft:
n1 = 960 rpm
n1 960
n2 = = = 266.67 rpm
u gear 3.6
n2 266.67
n3 = = = 130.72 rpm
uchain 2.04
n3 − nrequired 130.72 − 130
Rotational speed error: % = 100% = 100% = 0.55%
nrequired 130
• Calculating power for each shaft:
PI = 5 kW
PIII 5
PII = = = 5.32 kW
chain bearing 0.95 0.99
PII 5.32
PI = = = 5.54 kW
gear bearing 0.97 0.99
• Calculating torque:
PIII 9.55 106 5 9.55 106
TIII = = = 365284.58 Nmm
nIII 130.72
TIII 365284.58
TII = = = 179061.07 Nmm
uchain 2.04
TII 179061.07
TI = = = 49739.19 Nmm
ugear 3.6
4
� Motor I II III
P 5.54 5.54 5.32 5.00
u 3.60 2.04
n 960.00 266.67 130.72
T 49739.19 179061.07 365284.58
3. Design of bevel gear drive in speed reducer
3.1. Working life and allowable stress
Selecting material hardness for drive and driven gear: HB1 = 250 , HB2 = 228
NHO1 = 30HB12.4 = 30 3302.4 = 33.23 106 Cycles
NHO2 = 30HB22.4 = 30 3202.4 = 30.87 106 Cycles
Assuming the gears would be changed twice in their lifetime, required gear life:
3
Lh = 2 8 300 = 7200 hours
2
Equivalent operating cycles (static loading):
NHE 1 = 60cnLh
= 60 1 960 7200 = 414.72 106 (Cycles)
NHE 2 = 60cnLh
= 60 1 266.67 7200 = 115.2 106 (Cycles)
OH lim1 = 2HB1 + 70 = 2 330 + 70 = 730 MPa
OH lim = 2HB2 + 70 = 2 320 + 70 = 710 MPa
2
Life factor:
33.23 106 30.87 106
KHL1 = 6 = 0.79 K = 6 = 0.8
141.72 106 115.2 106
HL2
0.9KHL1 0.9 0.79
[ H1 ] = OH lim1 = 730 = 471.85 MPa
SH 1.1
5
� 0.9KHL2 0.9 0.8
[ H2 ] = OH lim2 = 710 = 464.72 MPa
SH 1.1
For bevel gears, [ H ] = 1.15 min([ H1 ],[ H 2 ]) = 534.43 MPa
3.2. Geometric calculations
Select gear width factor be = 0.285
beu 0.285 3.6
Assuming angular contact bearing: = = 0.6
2 − be 2 − 0.285
→ KH = 1.23
Preliminary calculations of outer diameter:
T1 xK H
de1 = 95 3
0.85(1 − 0.5 be )2 beux[ H ]2
49739.19 1.23
= 95 3
0.85(1 − 0.5 0.285)2 0.285 3.6 242.512
= 111.62 mm
Select de1 = 100,u = 3.6 → Z1 p = 17
→ Z1 = 1.6 Z1 p = 1.6 17 27 , select Z1 = 25 → Z2 = Z1 u = 25 3.6 = 90
de1 100
Outer module: me = = = 4 mm
Z1 25
Actual outer diameter: de1 = me Z1 = 4 25 = 100
de2 = me Z2 = 4 90 = 360
Pitch diameters: dm1 = de1 (1 − 0.5 be ) = 100(1 − 0.5 0.285) = 85.75 mm
6
�dm2 = de2 (1 − 0.5 be ) = 360(1 − 0.5 0.285) = 308.7 mm
Outer cone distance: Re = 0.5me Z12 + Z22 = 0.5 4 252 + 902 = 186.82 mm
Face width: b = Re be = 186.82 0.285 = 53.24 mm
Pitch angles:
1 1
1 = arctan = arctan = 15.52
o
u 3.6
→ 2 = 90 − 15.52 = 74.48
o o o
3.3. Kinematics and dynamics
dm1n1 85.75 960
Tangential velocity: v1 = 4
= = 4.31 m/s
6 x10 6 x104
→ Accuracy class 8 → KHv = 1.1
Force calculations:
2T1 2 49739.19
Ft 1 = Ft 2 = = = 1160 N
d m1 85.75
Fr 1 = Fa2 = Ft 1 tan cos 1 = 1160 tan20o cos15.52o = 406.81 N
Fr 2 = Fa1 = Ft 1 tan sin1 = 1160 tan20o sin15.52o = 112.97 N
3.4. Verification for contact stress
Select ZM = 275 (MPa1/2 ) for steel gears
Selecting ZH = 1.76 based on helical angle and ratio between (x1 + x2 ) / (Z1 + Z2 )
Axial contact ratio: = 0 (No helical angle)
7
� 4 − 4 − [1.88 − 3.2(1 / Z1 + 1 / Z2 )] 4 − [1.88 − 3.2(1 / 25 + 1 / 90)]
→ Z = = = = 0.87
3 3 3
Loading factor for contact stress: KH = KH KHv KH = 1 1.1 1.23 = 1.35
2T1K H (u2 + 1)
H = Z M Z H Z
0.85dm2 1bu
2 49739.19 1.35 (3.62 + 1)
= 275 1.76 0.87
0.85 85.752 53.24 3.6
= 526.77 MPa < [ H ] = 534.43 MPa
➔ Satisfactory
4. Design of roller chain drive
4.1. Choosing number of sprocket teeth Z
Z1 = 29 − 2u = 29 − 2 2.04 = 25
→ Z2 = Z1 u = 25 2.04 = 51
4.2. Calculating pitch pc
Selecting Z1 = 25 , → Z2 = Z1 u = 25 2.04 = 51
Dynamic load correction factor: Kr = 1.2
Center distance correction factor: Ka = 1
Orientation correction factor: K o = 1
Tension correction factor: Kdc = 1
Lubrication correction factor: Kb = 1.5
Operation shift correction factor: Klv = 1.12
→ Operation correction factor: K = 2.02
Z 01 25
Sprocket teeth coefficient factor: K z = = =1
Z1 25
8
� n01 200
Rotation speed coefficient factor: K n = = = 0.75
n1 266.67
KK Z K nP1 2.02 0.75 5.32
Pt = = = 8.06 kW
Kx 1
From calculated values, select pitch pc = 25.4 mm
4.3. Preliminary geometric calculations
Selecting center distance: a = 40 pc = 40 25.4 = 1016 mm
Calculating number of linkages based on center distance:
2
2a Z + Z Z − Z p
X = + 1 2 + 2 1 c
pc 2 2 a
2
2 1016 25 + 51 51 − 25 25.4
= + +
25.4 2 2 1016
= 118.43 → Select X = 118
Recalculating center distance with X = 118:
Z1 + Z 2 Z1 + Z 2
2
Z 2 − Z1
2
a = 0.25pc X − + X− − 8
2 2 2
25 + 51 25 + 51
2
51 − 25
2
= 0.25 25.4 118 − + 118 − − 8
2 2 2
= 1010.53 mm
Selecting a = 1008 mm , a = 2.02 4.04 mm
9
� 4.4. Kinematics and dynamics
n1 Z1 pc 266.67 25 25.4
Average velovity: v = = = 2.82 m/s
6 104 6 104
Tension due to centrifugal force: Fv = qmv12 = 2.6 2.822 = 20.67 N
1000P1 1000 5.32
Tangential force: Ft = = = 1886.52 N
v1 2.82
Shaft load: Fr = KmFt = 1.15 1886.52 = 2169.5 N (Km = 1.15 because incline is < 40o)
Initial tension: Fo = K f aqmg = 6 1008 2.6 9.8 = 154.1 N
4.5. Verification
P1K 5.32 2.02
Verify pitch: pc = 25.4 mm 600 3 = 600 3 = 22.64 , where
Z1n1 [ p0 ]K x 25 266.67 30 1
[p0] = 30 MPa based on the table below
Safety factor:
Q
s= [ s]
F1 + Fv + Fo
50000
= 8.9
1886.52 + 20.67 + 154.1
= 24.26 8.9
10
�[s] is selected based on rotational speed and pitch:
Impacts per second:
Z 1n1
i= [i ]
15 X
25 266.67
= [i ]
15 118
= 3.77 20
[i] is selected from the table below based on chain type and pc
4.6. Dimensions of sprockets:
Pitch diameters:
pc 25.4
d1 = = = 202.66 mm
sin sin
Z1 25
pc 25.4
d2 = = = 412.6 mm
sin sin
Z1 51
11
�Outer diameters:
da1 d1 + 0.7pc =202.66+0.7 25.4=220.44 mm
da2 d2 + 0.7pc =412.6+0.7 25.4=430.38 mm
5. Design of shafts in speed reducer
5.1. Shaft 1
Select C45 steel for shaft material → [ ] = 70 MPa
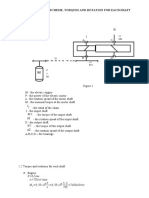
Free body diagram for shaft is as follow:
Point A connects to the motor, the bevel gear is mounted at point D.
Ft 1 = 1160 N , Fr 1 = 406.81 N
Ma1 = 0.5dm1 Fa1 =0.5 85.75 112.97=4847.59 N.mm
In Oyz plane:
{
M = −50R
/B y
C
− Ma1 + 80Fr 1 = 0
{
−50RyC − 4847.59 + 80 406.81 = 0 RyB = 147.13 N
{ C
F = −R
y
B
y + RyC − Fr 1 = 0 −RyB + RyC − 406.81 = 0 Ry = 553.94 N
In Oxz plane:
{
M /B = −50RxC + 80Ft 1 = 0
{
−50RxC + 80 1160 = 0
{
RxB = 696 N
F x = RxB − RxC + Ft 1 = 0 RxB − RxC + 1160 = 0 RxC = 1856 N
From the reaction forces above, the bending moment diagram can be drawn
12
�As well as the torque diagram:
13
�From the diagrams, critical section is at C, the equivalent moment is:
Mtd = Mx2 + My2 + 0.75T 2 = 348002 + 7356.52y + 0.75 49739.192 = 55862.76 N.mm
Mtd 55862.76
Therefore the diamter at section C: d 3 =3 = 19.98 mm
0.1[ ] 0.1 70
➔ Select dC = 20mm
Draft of shaft structure:
Base on diameter d = 15mm, select feather key size of 6mmx6mmx18mm
5.2. Shaft 2
Select C45 steel for shaft material → [ ] = 70 MPa
Free body diagram for shaft is as follow:
14
�Point A is where the sprocket will be mounted, the bevel gear at point D.
Ft 2 = 1160 N , Fr 2 = 112.97 N
Fr 3 = 2169.5 N (radial force by chain sprocket)
Ma2 = 0.5dm2 Fa2 =0.5 308 406.81=62791.12 N.mm
In Oyz plane:
{
M = −50R
/B y
C
+ Ma2 − 80Fr 2 = 0
{
−50RyC + 62791.12 + 80 112.97 = 0 RyB = 1188.04 N
{ C
F = −R
y
B
y + RyC + Fr 2 = 0 −RyB + RyC + 112.97 = 0 Ry = 1075.07 N
In Oxz plane:
{
M = −50F + 50R
/B r3
C
x + 80Ft 2 = 0
{
−50 2169.5 + 50RxC + 80 1160 = 0
{
RxB = 3643 N
F = −R + R + F
x
B
x
C
x t 2 + Fr 3 = 0 RxB − RxC + 1160 + 2169.5 = 0 RxC = 313.5 N
From the reaction forces above, the bending moment diagram can be drawn
15
�Mtd /B = Mx2 + My2 + 0.75T 2 = 1080922y + 0.75 179061.072 = 189026.5 N.mm
Mtd /C = Mx2 + My2 + 0.75T 2 = 348002 + 594022 + 0.75 179061.072 = 169666.7 N.mm
From the calculations, critical section is at B.
Mtd 189026.5
Therefore the diamter at section B: d 3 =3 = 30 mm
0.1[ ] 0.1 70
➔ Select dB = 30mm
16
�Draft of shaft 2 structure:
Base on diamter d = 25mm, select feather key size of 10mmx8mmx22mm
6. Selecting bearings for shafts
6.1. Pair 1 (shaft 1)
Since there is no axial load, selecting single-row deep groove ball bearing with bore
diameter of 20mm for the shaft.
Radial force at section B:
FrB = RBx 2 + RBy 2 = 6962 + 147.132 = 711.38 N
Radial force at section C:
FrC = RCx 2 + RCy 2 = 18562 + 553.942 = 1937 N
➔ Calculating with FrC
Select K = Kt = V = 1
17
�No axial load → X = 1,Y = 0
Dynamic equivalent load:
Q = (XVFrC + YFa )K Kt = FrC = 1937 N
Work life in million revolutions (3 years):
60nLh 60 960 14400
L= = = 829.44
106 106
Calculated dynamic load factor:
Ctt = Qm L = 1937 3 829.44 = 18199 N
Given the calculated variables, select the 6304 ETN9 bearing from SKF:
6.2. Pair 2 (shaft 2)
Since there is no axial load, selecting single-row deep groove ball bearing with bore
diameter of 30mm for the shaft.
Radial force at section B:
FrB = RBx 2 + RBy 2 = 36432 + 1188.042 = 3831.83 N
Radial force at section C:
FrC = RCx 2 + RCy 2 = 313.52 + 1075.072 = 1119.84 N
Moving on using FrB
Select K = Kt = V = 1
No axial load → X = 1,Y = 0
Dynamic equivalent load:
18
�Q = (XVFrB + YFa )K Kt = FrB = 3831.83 N
Work life in million revolutions, assume the bearings are changed twice in their life time:
60nLh 60 960 7200
L= = = 414.72
106 106
Calculated dynamic load factor:
Ctt = Qm L = 3831.83 3 414.724 = 28757 N
Given the calculated variables, select the 6306-Z bearing:
19