0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesTwo Cases in Solving Right Triangle
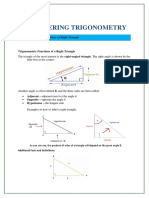
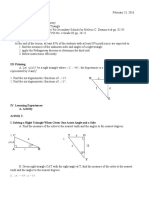
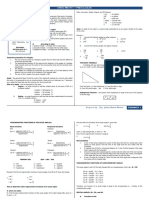
The document explains the process of solving right triangles by determining unknown parts using known sides and angles. It emphasizes that a right triangle can be solved with either two sides or one side and an acute angle, utilizing trigonometric functions and the Pythagorean Theorem. Two examples are provided for practical application, along with an activity for further practice in solving right triangles.
Uploaded by
elialleje083Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesTwo Cases in Solving Right Triangle
The document explains the process of solving right triangles by determining unknown parts using known sides and angles. It emphasizes that a right triangle can be solved with either two sides or one side and an acute angle, utilizing trigonometric functions and the Pythagorean Theorem. Two examples are provided for practical application, along with an activity for further practice in solving right triangles.
Uploaded by
elialleje083Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2