0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views2 pagesAI in Robotics Notes
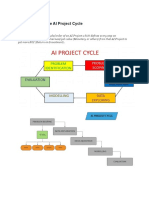
The document outlines the evolution of AI in robotics, highlighting key milestones and advancements from the mid-20th century to modern applications. It discusses the current state of AI-enabled robots, emphasizing their use of machine learning and real-time decision-making in various fields. Additionally, it describes the structure and functioning of intelligent agents, which are essential for achieving autonomy and adaptability in robotic systems.
Uploaded by
medhivya.raCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views2 pagesAI in Robotics Notes
The document outlines the evolution of AI in robotics, highlighting key milestones and advancements from the mid-20th century to modern applications. It discusses the current state of AI-enabled robots, emphasizing their use of machine learning and real-time decision-making in various fields. Additionally, it describes the structure and functioning of intelligent agents, which are essential for achieving autonomy and adaptability in robotic systems.
Uploaded by
medhivya.raCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2