0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesDbms-Assignment 1 2
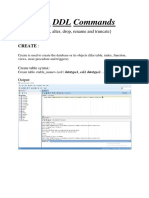
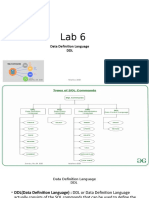
The document outlines the design and development of SQL DDL statements, focusing on SQL objects like tables, views, indexes, and synonyms. It explains the four types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL, with an emphasis on DDL commands such as CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. Additionally, it covers SQL constraints, the syntax for creating and managing database objects, and the importance of indexes and synonyms for efficient data retrieval.
Uploaded by
madarasarthakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views10 pagesDbms-Assignment 1 2
The document outlines the design and development of SQL DDL statements, focusing on SQL objects like tables, views, indexes, and synonyms. It explains the four types of SQL commands: DDL, DML, DCL, and TCL, with an emphasis on DDL commands such as CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. Additionally, it covers SQL constraints, the syntax for creating and managing database objects, and the importance of indexes and synonyms for efficient data retrieval.
Uploaded by
madarasarthakCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10