0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views9 pagesHow To Create A Hello World Program
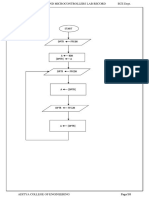
The document provides a series of assembly language programs demonstrating basic concepts such as creating a 'Hello, World!' program, conditional branching with BRP, BRZ, and BR instructions, arithmetic operations, if-then-else logic, string input/output, loops, summing numbers, and stack operations. Each program includes detailed explanations of the code lines and their functions. The examples illustrate fundamental programming techniques in assembly language.
Uploaded by
humayongujjar8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views9 pagesHow To Create A Hello World Program
The document provides a series of assembly language programs demonstrating basic concepts such as creating a 'Hello, World!' program, conditional branching with BRP, BRZ, and BR instructions, arithmetic operations, if-then-else logic, string input/output, loops, summing numbers, and stack operations. Each program includes detailed explanations of the code lines and their functions. The examples illustrate fundamental programming techniques in assembly language.
Uploaded by
humayongujjar8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 9