0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views14 pagesRobotic Assignment 3
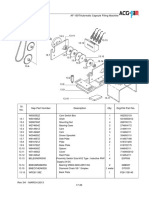
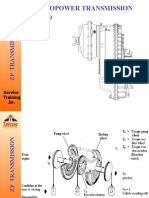
The document discusses the role of gears in robotic systems, highlighting their importance in controlling speed, torque, and direction of movement. It covers various types of gears, including spur, bevel, and planetary gears, and their applications in robotics. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of gear ratios in enhancing torque, precision, and overall performance of robots.
Uploaded by
drakenboy401Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views14 pagesRobotic Assignment 3
The document discusses the role of gears in robotic systems, highlighting their importance in controlling speed, torque, and direction of movement. It covers various types of gears, including spur, bevel, and planetary gears, and their applications in robotics. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of gear ratios in enhancing torque, precision, and overall performance of robots.
Uploaded by
drakenboy401Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 14