0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views23 pagesData WH Architecture
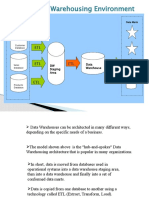
Data warehouse architecture defines the structure for data communication and processing within an enterprise, featuring standard components like operational systems, flat files, and metadata. Common architectures include basic, with staging areas, and with data marts, each serving different data processing needs. Key properties of data warehouse architectures include separation of processes, scalability, extensibility, security, and administrability, with various tiered architectures (single, two, and three-tier) designed to optimize data management and analysis.
Uploaded by
basitalictn786Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views23 pagesData WH Architecture
Data warehouse architecture defines the structure for data communication and processing within an enterprise, featuring standard components like operational systems, flat files, and metadata. Common architectures include basic, with staging areas, and with data marts, each serving different data processing needs. Key properties of data warehouse architectures include separation of processes, scalability, extensibility, security, and administrability, with various tiered architectures (single, two, and three-tier) designed to optimize data management and analysis.
Uploaded by
basitalictn786Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23