0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views8 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Science (Single Award) Physics Revision Guide
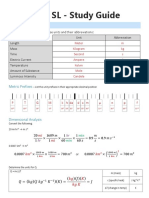
The Edexcel IGCSE Science (Single Award) Physics Revision Guide covers essential concepts in physics, including forces, motion, electricity, waves, energy resources, and astrophysics. It provides key formulas, examples, and explanations for topics such as acceleration, Ohm's Law, wave properties, and nuclear processes. The guide emphasizes the importance of understanding units of measurement and the relationships between different physical quantities.
Uploaded by
9yjwsmk4xkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views8 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Science (Single Award) Physics Revision Guide
The Edexcel IGCSE Science (Single Award) Physics Revision Guide covers essential concepts in physics, including forces, motion, electricity, waves, energy resources, and astrophysics. It provides key formulas, examples, and explanations for topics such as acceleration, Ohm's Law, wave properties, and nuclear processes. The guide emphasizes the importance of understanding units of measurement and the relationships between different physical quantities.
Uploaded by
9yjwsmk4xkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8