0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesPython Unit1 Unit2 Viva QA
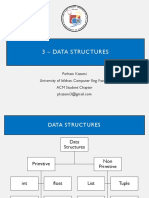
The document provides an overview of Python basics and data structures, including Jupyter Notebook usage, script execution, comments, variables, data types, and control flow statements. It also covers string manipulation, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets, detailing their creation, modification, and key operations. Key concepts such as namespaces, scope, and lambda functions are also explained.
Uploaded by
preksha11bolampalliwarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesPython Unit1 Unit2 Viva QA
The document provides an overview of Python basics and data structures, including Jupyter Notebook usage, script execution, comments, variables, data types, and control flow statements. It also covers string manipulation, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets, detailing their creation, modification, and key operations. Key concepts such as namespaces, scope, and lambda functions are also explained.
Uploaded by
preksha11bolampalliwarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3