0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views30 pagesIntroduction To Embedded Systems Unit 1
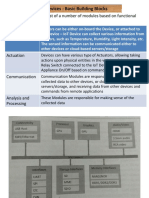
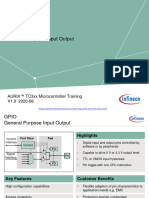
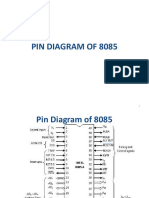
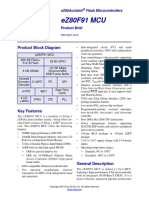
This document provides an introduction to embedded systems, focusing on the Raspberry Pi, its models, specifications, and comparisons with microprocessors and microcontrollers. It outlines the definition, types, and key characteristics of embedded systems, as well as programming languages used in their development. Additionally, it details the Raspberry Pi's features, technical specifications, and various peripherals such as displays and input devices.
Uploaded by
musalesuman7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views30 pagesIntroduction To Embedded Systems Unit 1
This document provides an introduction to embedded systems, focusing on the Raspberry Pi, its models, specifications, and comparisons with microprocessors and microcontrollers. It outlines the definition, types, and key characteristics of embedded systems, as well as programming languages used in their development. Additionally, it details the Raspberry Pi's features, technical specifications, and various peripherals such as displays and input devices.
Uploaded by
musalesuman7Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 30